Aria ionizzata fa bene, perché ?
La ionizzazione dell'aria è un parametro che acquista sempre maggiore importanza dal punto di vista ambientale, per gli effetti biologici che comporta e per la vasta gamma di applicazioni nelle più svariate discipline tecnico-scientifiche
(1). Il problema dell'esatta misura degli ioni atmosferici e di viva attualità poiché le metodiche portano a risultati non sempre concordanti (2). L'inquinamento elettrico ed elettromagnetico inducono azioni dannose sugli esseri viventi e sull’assetto biocenotico () di un Climax (), soprattutto attraverso variazioni della concentrazioni di ioni atmosferici (2). In defintiva il pullulare di linee elettriche, ripetitori, radiotrasmettitori, elettrodomestici, genera nello spazio una tale massa di cariche elettriche e magnetiche da determinare disturbi i più vari: astenia, cefalea, insonnia, nervosismo, sino a condizioni di estrema gravità. Anche se in disaccordo con vari organismi internazionali, alcuni ricercatori ritengono che le variazioni ioniche prodotte nell'ambiente dai campi elettrici e magnetici, possano modificare importanti sistemi di controllo omeostatico (ad esempio il rilascio di melatonina e di conseguenza sia il ritmo sonno-veglia che l'attività dei linfociti Natural Killer), ingenerando disturbi molto seri, prima funzionali ed infine anche organici (3).
Generando una sorta di "vento magnetico" essi risulterebbero in grado di cariche l'ambiente di ioni positivi, certamente dannosi per la salute umana, con ripercussioni sull'umore (riduzione della serotina e depressione) ed anche sull'equilibrio organico generale (accumulo di radicali liberi) (4). Intelligentemente la dott.ssa Comerio (5) ha già analizzato l’aggressione prodotta dai campi magnetici alla luce dei classici cinesi (Sowen e Shang Han Lun, soprattutto), ma il nostro scopo è quello di mostrare che le xie prodotte sotto forma di ioni e radicali, inducono una doppio "eccesso", contrassegnato da "Vento Esterno" e "Calore Interno" (con conseguente esuberanza di Yang e depauperamento progressivo di Yin, Jing e Sangue) (6-8).
Fin dagli anni settanta degli studi in lingua inglese hanno dimostrato che i campi elettrici e magnetici modificano il livello ed il tipo di ioni nell'ambiente circostante (9-10). Nella seconda metà degli anni settanta su Science (11) si è potuto dimostrare che esiste una precisa relazione fra morti per malattie cardiovascolari () e variazioni mensili d’elettromagnetismo. L'insieme dei dati sperimentali raccolti ci permette di affermare che i piccoli ioni negativi sono in grado di regolare al meglio i sistemi di controllo omeostatico, mentre gli ioni positivi producono variazioni di neurormoni e neurostrasmettitori (serotonina, noradrenalina, adrenalina) che inducono dapprima disturbi psicologici e poi malattie immunitarie o d’altro genere (12). Al pari dei "venti caldi"() che percorrono la terra e come le "macchie solari", i campi elettrici ed elettromagnetici caricano l'ambiente di ioni positivi producendo (per riduzione di catecolamine ed incrememento di 5-idrositriptamina) depressione, sonnolenza, apatia, cui seguono facilità alle infezioni, turbe immunitarie ed anche neoplasie (2,4,12).
Pertanto quello che potremmo definire "vento elettro-magnetico" induce una condizione di depauperamento progressivo, indipendentemente dai valori di produzione-distribuzione, di Energia Difensiva, con tutta una serie d’evidenti conseguenze per l'organismo. Prova diretta di questo è l'incremento del potere battericida dell'organismo se sottoposto all'azione di aeroionizzatori ad emissione di piccoli ioni negativi (13-14).
Di fronte ad individui i quali, senza altra causa apparente né congenita né acquisita (farmaci, HIV, diabete, ecc. ()) presentano riduzione d'efficienza immunitaria con vaghi disturbi neuropsichici (depressione, apatia, ecc.), si può presumere una quadro di eccessiva esposizione a campi magnetici a bassa frequenza (uso di telefonini, termocoperte, apparecchiature elettriche attive nelle camere da letto, ecc.).
Bibliografia
1. Nappi G., Maschicchi M.M., Calcaterra P., De Luca, De Luca S.: Studio sul parametro "ionizzazione dell'aria" nelle palestre dell'ISEF in Lombardia, Med. Clin. e Term., 1992, 18:43-50.
2. Marinelli F., Garcia A., Lozzio A., Valenzia V.I.: Clima e bioclimatologia marina: progressi e considerazioni sulla ionizzazione dell'aria e i campi elettromagnetici, materiale scientifico EURODREAM, La Spezia, 1999.
3. Iriki M.: Editorial, Journal of Biometereology, 1996, 1: 1-3.
4. Roberts G.F. & Anderson R.: La formula Everet Storey, Ed. Health Dimension, South-Oregon, 1999.
5. Comerio M. C.: Campi Elettromagnetici e salute umana, XX Congresso SIA, Firenze, 13-14 ottobre 2000, Atti.
6. De Berardinis D., Di Stanislao C., Corradin M., Brotzu R.: Organi e Visceri in Medicina Cinese, Ed. Sanli/Bimar, Roma, 1992.
7. Roustan C.: Traité d'Acupuncture, vol I, Ed. Masson, Paris, 1980.
8. Carnilot P. (Ed.): Acupuncture et Médicine Chinoise, Encyclopedie de Medicine Naturelle, Tome I, Ed. Techiniques, Paris, 1989.
9. Llaurado J.C., Sances A., Battocletti A.: Biological and Clinical Effects of Low-Frequency Magnetic and Electric Fields, Ed. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, 1974.
10. Soyka F. & Edmonds A.: The Ion Effects, Ed. Bantam, New York, 1977.
11. Kreuger A.P. & Reed J.: Biological Impact of Small Air Ions, Science, 1976, 193: 1209-1213.
12. Rosenthal N.E.: Winter Blues, National Institute of Mental Health, New York, 1990.
13. Gabbay J.: Effect of ionization on microbial air pollution in the dental clinic, Environ. Res., 1990, 52(1): 99-105.
14. Mitchell B.W.: Effect of negative air ionization and airborne trasmission of Newcastle disease Virus, Av. Dis., 1994, 38(4): 725-732.
note
Biocenotico è il complesso di organismi viventi presenti in un certo ambiente. Vedi:
- Soyka F.: Effects of ions, Ed. Lester and Open, Lichester, 1977.
- AAVV: Dizionario medico illustrato Dorland, Ed. Farmitalia-Sigma Tau, Milano-Roma, 1987.
Si definisce Climax l'equilibrio di organismi animali e vegetali posti nello stesso ambiente. Vedi: AAVV: Dizionario Medico, Ed. Zanichelli, Bologna, 2001.
L'infarto miocardico è definito "Vento del Cuore". Vedi: Ming O. (chef ed.): Chinese-English Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ed. Joint Publication, Hong Kong, 1989.
Definiti con vari toponimi: lo scirocco in Italia, il maestrale in Francia, il foen in Svizzera, lo sharav in Medioriente, il northelies in Austria e i westerlies nel Nuovo Galles e nel Queensland, tutti in grado di provocare cicloneurosi con ansia, insonnia, depressione, nervosismo, tachicardia, ecc. Vedi
- Favilli U. (a cura di): Trattato di Patologia Generale, I Ed., Ed. Casa Editrice Ambrosiana, Milano, 1974.
- Lucchese M. (a cura di): Dizionario Medico Inglese-Italiano, Ed. Raffaello Cortina, Torino, 1986.
Si leggano:
- Lourencini da Silva R. , Albano F., Lopes dos Santos L.R. , Tavares A.D., Felzenszwalb I.:
The effect of electromagnetic field exposure on the formation of DNA lesions, Redox Rep., 2000, 5(5): 299-301.
- Pascual-Leone A., Walsh V., Rothwell J.: Transcranial magnetic stimulation in cognitive neuroscience--virtual lesion, chronometry, and functional connectivity, Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2000,10(2):232-237. 7
Vedi: Van Monttford J.C.: Immunotherapie, Ed. Ankh-Hermes, Deventer, 1990.
"La ionizzazione dell'aria nel controllo della IAQ"
Tra i parametri che influiscono sulla qualitàdell'aria negli ambienti chiusi, non va dimenticato il campo elettricoambientale determinato dagli ioni in sospensione. Mezzi artificiali possonopermettere di ristabilire un equilibrio ionico ottimale alterato
________________________________________
Il benessere di chi occupa uno spazio chiuso, come si sa, è uno stato soggettivo: non tutti siamo sensibili allo stesso modo al variare dei parametri ambientali come temperatura,umidità relativa, grado di pulizia dell'aria, illuminazione, rumore. Inoltre, certe condizioni particolari (umore, stress, attività,modo di vestire) possono influire pesantemente sulla personale condizione di benessere. Perciò, dato un certo ambiente, definito "confortevole"secondo tutti i normali parametri delle norme di buona progettazione ecostruzione, si troverà comunque una certa percentuale di persone che si sente a disagio. A volte, stranamente, questa percentuale diventa particolarmente elevata, molto superiore ai valori statisticamente attesi.Ciò significa che deve esserci un qualche altro parametro ambientale al quale gli esseri umani sono più o meno sensibili, parametro che normalmente non viene tenuto in considerazione in sede di norma e di progetto.Esistono numerosi indizi e qualche prova a carico di due importanti fattori ambientali:
• la ionizzazione dell'aria, intesa siacome quantità assoluta di ioni che come percentuale relativa tra ioni positivi e negativi;
• la presenza di campi elettromagnetici di varia frequenza ed intensità.
In particolare in questa sede ci si occuperà della ionizzazione dell'aria, sulla quale è possibile intervenire con mezzi relativamente semplici.
La ionizzazione naturale dell'aria
L'esistenza di un campo elettrico atmosferico divenne evidente per Benjamin Franklin un giorno del 1750, trascinando un aquilone tra le nubi nel bel mezzo di un temporale. In questo modo Franklin sperimentò anche l'effetto più imponente della ionizzazione atmosferica sull'organismo, la folgorazione. Una trentina d'anni più tardi, Bertholon si accorse che alcuni fenomeni atmosferici (i venti caldi phœn, sharav, scirocco) non solo erano causa di imponenti variazioni del campo elettrico dell'aria , ma parevano influenzare lo stato di salute delle persone. Nel 1899 Elster e Geitel dimostrarono per mezzo di sensibili elettroscopi la presenza nell'aria di particelle cariche positivamente e negativamente, di dimensioni molecolari, che vennero chiamate "ioni".Da allora in poi i lavori di numerosi ricercatori hanno permesso di chiarire la situazione elettrica dell'atmosfera (fondamentali i lavori di Langevin,1905).
Grossolanamente, le particelle elettricamente cariche che costituiscono il campo elettrico atmosferico sono le seguenti - fig.1
1. piccoli ioni leggeri; formati da molecoledi gas atmosferici che hanno perso (ioni positivi) o acquisito (ioni negativi)una o più cariche elettriche elementari (elettroni), per mezzo dell'azionedi fenomeni ionizzanti naturali, come i raggi cosmici, i raggi ultravioletti,la radioattività naturale. Caratterizzati da una elevata mobilità,sono preponderanti negli spazi aperti ed incontaminati;
2. grandi ioni pesanti; formati dalla agglutinazione di numerosi piccoli ioni sulla superficie di goccioline d'aerosol o di particelle solide. Sono tipicamente abbondanti nelle zone industrializzate ed affollate.
Numerosi lavori sperimentali hanno permesso di rilevare le concentrazioni ioniche presenti nei vari ambienti Tab.1,evidenziando le correlazioni tra situazione elettrica dell'atmosfera e stato di salute delle popolazioni esposte. In estrema sintesi, si può dire che la situazione ideale di benessere corrisponde ad una concentrazione ionica di 1800 piccoli ioni per cm3 d'aria, suddivisi tra positivie negativi con un rapporto di 0.8 a 1. Le sensazioni di disagio e di malessere sono invece correlate ad un eccesso di ioni positivi, come ad esempio accade in seguito a fenomeni meteorologici particolari, come la presenza di venti caldi ed asciutti (Scirocco, Fœhn, Sharav, nomi che la tradizione popolareda sempre associa a malanni fisici e psichici) oppure nell'imminenza di temporali (come ben sanno le persone cosiddette "meteoropatiche", particolarmente sensibili al peggioramento delle condizioni atmosferiche).
La ionizzazione dell'aria negli ambienti chiusi
Negli ambienti chiusi, la situazione ionica dell'aria è ben lontana dai valori ideali; infatti al chiuso sono preponderanti le fonti di ionizzazione positiva, mentre l'inquinamento indoor di origine organica ed inorganica porta alla formazione dei grossi ioni a discapito dei piccoli , che si trovano in quantità estremamente limitata. Nell'ambito della Indoor Air Quality, la ionizzazione dell'aria è un aspetto spesso dimenticato, oppure affrontato in modo improprio,con conseguenze non trascurabili. Nella maggior parte dei casi dove è presente un impianto canalizzato di trattamento dell'aria, questo stesso impianto è fonte di inconvenienti correlati alla ionizzazione dell'aria. Tutti conosciamo i caratteristici depositi nerastri in corrispondenza delle bocchette di diffusione dell'aria nell'ambiente: la loro presenza non solo è indice della presenza di particolato, ma è una conseguenza della ionizzazione dell'aria per frizione lungo le condotte, che provocala cessione della carica alle particelle in sospensione e la loro precipitazione. Per minimizzare questo fenomeno, è conveniente utilizzare condotte metalliche connesse all'impianto di messa a terra dell'edificio, assicurandola continuità elettrica tra sezioni diverse della canalizzazioneeventualmente isolate da guarnizioni per mezzo di collegamenti con trecciain rame o cavo elettrico di sezione adeguata. E' possibile inoltre intervenire installando, nel tratto di condotta in prossimità delle bocchette,speciali dispositivi in grado di eliminare le cariche elettrostatiche per mezzo di un campo elettrico alternato ad alta tensione, oppure generando una carica di segno opposto che neutralizzi l'eccesso di ionizzazione (lo sfregamento nelle canalizzazioni ionizza l'aria positivamente; quindi l'aggiunta di cariche negative ha un effetto neutralizzante). L'intervento più corretto e razionale consiste nell'installazione di filtri adeguati per bloccare il particolato, correggendo inoltre l'equilibrio ionico alterato con emettitori elettronici di anioni (ioni negativi). E' da sottolineare che l'installazione di emettitori di anioni da soli, senza eliminare il particolato, ha un effetto deleterio: le particelle in sospensione vengono prima neutralizzate, poi caricate negativamente provocandone comunque la precipitazione sulle superfici degli ambienti. E' dunque assolutamente necessario eliminare i grossi ioni inquinanti costituiti dal particolato e dall'aerosol in sospensione, in modo da permettere la vita e la diffusione dei piccoli ioni utili a ricreare il corretto equilibrio elettrico ambientale. Nell'abiente esterno, come visto precedentemente, una situazione ideale è rappresentata da una concentrazione di circa 2000 piccoli ioni per centimetro cubo d'aria, con una leggera prevalenza di ioni negativi:per ricreare la stessa situazione negli ambienti chiusi, generalmente è indicata l'immissione di quantità calibrate di ioni negativi, per contrastare l'eccesso di ioni positivi provocato dallo sfregamento dell'aria sulle superfici (vetro, plastica) e dall'utilizzo in ambiente di macchine ad alta tensione positiva (televisori, monitor per computers, videoterminali,fotocopiatrici e stampanti laser). Come nel caso dell'aria emessa dalle bocchette, anche per l'atmosfera ambientale è indispensabile eliminare gli inquinanti che possono formare grossi ioni e precipitare sulle superfici,oppure essere respirati dagli occupanti. Con un progetto accurato, ovesia possibile, ciò può essere fatto per mezzo dell'impiantodi condizionamento canalizzato, dotato di filtri appropriati sull'aria primaria e di ripresa, nonchè di dispositivi generatori di anioni(ioni negativi), in prossimità delle bocchette di immissione. Dovenon si possa ricorrere all'impianto canalizzato, sarà indicato l'impiegodi appositi purificatori, in grado di aspirare l'aria carica di inquinanti reimmettendola quindi nell'ambiente pura e bilanciata ionicamente, peril massimo confort degli occupanti.
Figura 1
Meccanismo di formazione dei grandi e piccoli ioni secondoLangevin: le radiazioni ionizzanti agiscono sulle molecole dei gas atmosferici,provocando la formazione di una molecola ionizzata positivamente e di unelettrone. Quest'ultimo viene acquisito da una molecola neutra formando una molecola ionizzata negativamente. Le molecole ionizzate formano i piccoli ioni, i quali, aggregandosi a grosse particelle neutre in sospensione nell'aria(aerosol, particolato), formano i grossi ioni, detti di Langevin. I piccoli e i grossi ioni negativi e positivi possono, ricombinandosi, originare piccole e grandi particelle neutre.
Ambiente ioni positivi per cm3 ioni negativi per cm3 rapporto ioni + / -
Ambiente terapeutico 1000 9000 0,1:1
Aria di montagna 2500 2000 1,25:1
Ambiente rurale 1800 1500 1,2:1
Ambiente urbano 600 500 1,2:1
Atmosfera pre-temporalesca 3000 800 3,75:1
Atmosfera post-temporalesca 800 2500 0,32:1
Industria leggera 400 250 1,6:1
Ufficio / appartamento 200 150 1,33:1
Piccoli locali 80 20 4:1
Veicoli mobili chiusi 80 20 4:1
Situazione ottimale 800 1000 0,8:1
Tabella 1,
Tipiche concentrazioni ioniche in ambienti e situazioni diverse: come si vede, gli ambienti chiusi sono generalmente poveri di ioni, con una netta prevalenza di ioni positivi. Significativo il fatto che il rapporto ioni positivi / negativi in alcuni locali sia molto simile a quello della atmosfera pre-temporalesca, associata notoriamente a sensazioni di ansia e di disagio.
Figura 2
Lungo le canalizzazioni l'aria viene caricata positivamente per attrito;in questo modo vengono elettrizzate le particelle in sospensione che si depositano in prossimità delle bocchette: inoltre vengono diffusi ioni positivi in eccesso nell' ambiente. Per ovviare a questi inconvenienti,le condotte devono essere messe a terra, l'aria deve essere filtrata efficacemente ed arricchita di ioni negativi prima dell'immissione nel locale.
Figura 3
In assenza di impianto canalizzato, per ripristinare un corretto equilibrio ionico è necessario utilizzare un purificatore-ionizzatore in grado di aspirare l'aria inquinata e reimmetterla nell'ambiente pulita ed arricchita di anioni. Gli apparecchi più moderni attivano automaticamente laionizzazione solo dopo la completa rimozione del particolato.
Bibliografia
G.W.K. King, Air ionization and itseffects on well being and stress and its biological effectcs, AIBC Bulletin,vol. 2, n° 2, American Institute of Biomedical Climatology, June 1989
G.R. Rager (a cura di), AA.VV., Problèmesd'ionisation et d'aero-ionisation, Maloine S.A. èditeur, Paris,1975
I Benefici degli ioni negativi
Tutto sugli ioni
Gli ioni sono delle particelle cariche nell'aria che si formano quando una dose sufficiente di energia agisce su una molecola, come il diossido di carbonio, l'ossigeno, l'acqua o l'azoto per emettere un elettrone dalla molecola rilasciando uno ione caricato positivamente. L'elettrone spostato si attacca ad una molecola vicina, che diventa quindi uno ione caricato negativamente. E' lo ione negativo dell'ossigeno quello che più ci influenza. Avete presente la sensazione che si prova vicino ad una cascata o in alta montagna? Questi sono due posti dove si trovano migliaia di ioni negativi. Essi hanno effetto sulla biochimica umana.
Normalmente il numero degli ioni nell'aria fresca di campagna è da 2000 a 4000 ioni negativi per centimetro cubo (circa le dimensioni di una zolletta di zucchero). Alle cascate Yosemite, sperimentereste più di 100,000 ioni negativi per centimetro cubo. D'altra parte, il livello è molto al di sotto di 100 per centimetro cubo sulle autostrade di Los Angeles nelle ore di punta.
Mentre la ionizzazione dell'aria è obbligatoria in molti ospedali e luoghi di lavoro europei e russi, nel nostro Paese è venuta alla luce solo recentemente, con la crescita del problema dell'aria tossica negli ambienti urbani.
"Ioni e consapevolezza" Whole Self, Primavera 1991
Cause della carenza di ioni negativi
La ricerca ha dimostrato che le aree inquinate sia al chiuso che all'aria aperta hanno dei livelli molto bassi di ioni negativi, e livelli molto alti di ioni positivi. Sembrerebbe che tutti o quasi gli ioni negativi disponibili si fossero esauriti nella loro lotta con gli agenti contaminanti. Anche i venti caldi e secchi come il Santa Ana o i venti Witches (letteralmente “venti delle streghe” n.d.t.) privano l'aria degli ioni negativi.
Effetti dell'esposizione agli ioni negativi
Degli studi hanno dimostrato che alcune persone diventano molto depresse quando il numero degli ioni negativi è molto basso (depressione stagionale).
Un'alta esposizione agli ioni negativi sembrava associata al sentirsi meglio con se, meno sensibili e più ricettivi o tonici (energizzati).
"Aviazione, spazio e medicina ambientale", Agosto 1982.
I risultati indicavano che i soggetti avevano tempi di reazione più veloci ed avevano riferito di sentirsi significativamente più energici in condizioni di ioni atmosferici negativi rispetto a condizioni di aria normali.
"L'influenza degli ioni atmosferici negativi sulla prestazione umana e sull'umore"
L'introduzione di un generatore di ioni negativi ha aumentato i tassi soggettivi di vigilanza, la freschezza atmosferica e il calore ambientale e personale. Gli ioni hanno ridotto l'ansia, la tensione e li hanno aiutati a respirare più facilmente.
"L'effetto ione"
Dr. Bob Arnot
"Se i burrascosi venti invernali che soffiano attraverso la nazione questa settimana ti stanno buttando giù, c'è una buona ragione. I ricercatori ora credono che i venti “cattivi” caccino via delle particelle subatomiche altamente cariche che si chiamano ioni negativi dall'aria intorno a noi, contribuendo ad una forma stagionale di depressione. Ecco perché. I livelli di una sostanza chimica cerebrale responsabile dell'umore che si chiama serotonina, sono spesso più bassi nei casi di depressione stagionale. I livelli di serotonina possono essere aumentati attraverso una maggiore esposizione alla luce o con antidepressivi come il Prozac. I ricercatori dicono anche che gli ioni negativi possono aumentare i livelli cerebrali di serotonina.
Uno studio riportato nel numero corrente della “Rivista di medicina alternativa e complementare” ha concluso che il 58 percento dei pazienti trattati con ioni negativi ad alta densità hanno avuto un significativo sollievo nei loro sintomi, quasi identico al numero di miglioramenti riscontrati con i farmaci, ma senza gli effetti collaterali degli stessi.
Trascrizione del notiziario della CBS del 14/2/95 6:30-7:00 PM, con Connie Chung.
L'introduzione di un generatore di ioni negativi ha aumentato il tasso soggettivo di vigilanza, la freschezza atmosferica ed il calore ambientale e personale. Gli ioni hanno ridotto il tasso di lamentele di mal di testa del 50% e ridotto significativamente il numero di disturbi di nausea e vertigini.
L'influenza degli ioni atmosferici, della temperatura e dell'umidità sul benessere e sull’agio soggettivi.” Rivista di psicologia ambientale, Dicembre 1981.
Sono stati studiati gli effetti della ionizzazione positiva o negativa artificiale dell'aria sullo svolgimento di compiti psicomotori su 25 uomini in buona salute dai 18 ai 26 anni. Sono stati usati 3 ambienti di prova : naturale, con ionizzazione negativa e con ionizzazione positiva. Alla ionizzazione negativa si è associato un significativo incremento delle prestazioni rispetto ai controlli.”
"Gli ioni atmosferici e la prestazione umana" Ergonomics, aprile 1978.
10 Radioattività ambientale e dose annua assorbita
Anteprima della sezione
Nell’ambiente esiste un fondo di radioattività naturale generato dai raggi cosmici e dagli elementi radioattivi naturali presenti nelle rocce e nella biosfera. Il contributo più importante, pari a circa il 52%, a questo fondo di radioattività dell’ambiente si deve all’uranio 238 e ai suoi discendenti della serie radioattiva di cui è capostipite, in particolare il radon. Il 16,6% circa è ascrivibile invece al torio 232 e ai suoi discendenti; il 15% a isotopi quali il potassio 40 e il rubidio 87, e un altro 15% ai raggi cosmici, che, benché schermati dagli strati alti dell’atmosfera, penetrano in minima percentuale fino alla biosfera. Il totale corrisponde a una dose di circa 130 mRem all’anno.
Se si vuole calcolare la dose a cui un essere umano è normalmente soggetto, tuttavia, si deve aggiungere una componente dovuta alle eventuali esposizioni a radiazioni artificiali: quelle provenienti da radioterapie e analisi radiologiche (circa 46 mRem all’anno), quelle immesse nell’ambiente dai test nucleari (circa 2 mRem all’anno), quelle riconducibili all’attività delle centrali nucleari (circa 0,2 mRem all’anno). Questi contributi portano la dose annua assorbita a circa 200 mRem all’anno. Per avere un’idea degli effetti che queste dosi possono sortire sull’organismo, si consideri che una quantità di radiazioni compresa tra 0 e 25 Rem (1 Rem = 1000 mRem) non produce in genere alcun effetto osservabile; tra 25 e 100 Rem si osservano piccole variazioni nella composizione del sangue; tra 100 e 200 Rem si avverte nausea e affaticamento, oltre a sostanziali variazioni della composizione del sangue e, in pochissimi casi, la morte; si ha invece alta possibilità di morte per dosi superiori ai 200 Rem.
PREMESSA
Cap.1
Da tempo nei Paesi più attenti e sensibili alla problematica della " salubrità ambientale" negli spazi abitati, sono stati presi in considerazione tutti quei parametri legati ai fenomeni elettrici e magnetici che oggi ( alla luce dei progressi compiuti in campo medico e scientifico ) come ben sappiamo rivestono molta importatanza per la nostra salute.
E' infatti da ritenersi incompleta quell'analisi della qualità dell' aria , o comunque della vita all'interno delle abitazioni , che non tenga conto di tutti i parametri che intervengono in modo più o meno rilevante nelle modificazioni del sistema stesso.
Purtroppo ancora oggi vi sono Paesi , tra i quali I'Italia , in cui le conoscenze scientifiche riguardanti queste problematiche non vanno oltre il livello di ricerca; al contrario in altri Paesi ( U.S.A. , Norvegia , Svezia , Danimarca ecc) vengono seriamente tenute in considerazione dagli Enti e dagli Istituti preposti ai controlli ed allo studio delle condizioni di vita della popolazione, e quindi tradotte in una serie di misure di prevenzione atte a diminuire i rischi per la salute
BIOLOGIA ARCHITETTONICA.
Cap. 2
Troppo spesso si studiano e si analizzano le varie componenti dei sistemi e delle strutture abitative, senza tenere conto che vi sono altri " agenti inquinanti " oltre agli ossidi di azoto , alla formaldeide , al pentaclorofenolo ecc . , o dimenticando che i parametri fisici ed ambientali che definiscono il grado del comfort abitativo non sono solo temperatura , umidità , e movimento d' aria.
E' infatti emerso, da numerosi studi e ricerche condotte negli U.S.A. e nei Paesi del Nord Europa ,che esiste un rapporto diretto tra alcune malattie e disturbi accusati da persone che passano la maggior parte del loro tempo in luoghi chiusi ( uffici , fabbriche , magazzini ... ) , e la presenza di forti squilibri elettrici ( campi elettromagnetici, elettropulsanti ed elettrostatici , radiazioni ionizzanti di basso livello inversioni della carica spaziale con predominanza aero ionica di polarità positiva).
Proprio per questo motivo, nei Paesi in cui le conoscenze in campo di inquinamento ambientale sono più evolute , con il termine BIOLOGIA ARCHITETTONICA si indica quella branca della scienza che studia le azioni e le interazioni biologiche tra 1' uomo e lo " spazio - struttura " abitativa.
Appare infatti evidente la differenza che esiste tra una costruzione tradizionale ed un palazzo di cemento armato in una grossa città ; la naturale presenza di energia elettro-magnetica quanto meno viene alterata dalle strutture artificiali sopracitate che , a volte , possono rivelarsi dei veri e propri bunker elettrici.
Non solo, ma è molto importante tenere in considerazione che individuare il giusto grado di umidità e di temperatura non implica necessariamente I'aver stabilito le condizioni microclimatiche soddisfacenti e confortevoli per gli occupanti; come detto vi sono altri fattori climatici che devono essere considerati.
CARATTERISTICHE FISICHE DELLA IONIZZAZIONE.
Cap. 3
La ionizzazione dell'aria è il fenomeno fisico di scissione di un atomo , o di una molecola , in più parti dotate di carica elettrica la cui somma algebrica è nulla.
Innanzitutto è indispensabile sottolineare che la ionizzazione è un fenomeno naturale che interviene spontaneamente ogni qualvolta una molecola è sottoposta all'azione di un processo energetico in cui la quantità totale di energia ( Et ) e' superiore al valore di Ei ( Energia di ionizzazione ) della molecola stessa.
Quando una radiazione incidente ( con Et > Ei ) entra in collisione con un atomo, lo scambio energetico che si verifica è sufficiente ad estrarre un elettrone dall'orbita più esterna e, a causa dello squilibrio elettrico 1'atomo assume una carica Positiva ( AEROIONE + ) . L'elettrone invece, liberato dal suo legame con il nucleo si fissa immediatamente su un altro atomo che quindi assume una carica Negativa ( AEROIONE - ).
I processi ( o agenti ionizzanti ) che possono indurre la ionizzazione dell'aria sono molteplici:
- Emanazioni radioattive (raggi gamma e raggi X )
- Raggi Cosmici.
- Radiazioni U.V.
ed inoltre :
- Collisioni ed Urti tra corpuscoli dotati di energia cinetica ( ionizzazione d'urto ).
- Emissioni di fotoelettroni, termoelettroni, fiamme scariche elettriche, frizione molecolare ...
- Fattori e parametri elettro meteorologici e climatologici.
Dipendentemente dalla saturazione della corona periferica ogni atomo ha una probabilità ben definita di assumere una carica elettrica positiva o negativa.
Gli ioni atmosferici (o aeroioni) si possono classificare in trè categorie :
- PICCOLI
Sono composti da piccoli "grappoli" di molecole (diametro 0.001 - 0.003 micron ) con grande mobilità ed una carica elettrica elementare di 1.6*10 E-9 Coulomb. Hanno una vita media molto breve soprattutto in presenza di umidità.
- INTERMEDI
Sono costituiti da grossi agglomerati molecolari con diametro di 0.003 - 0.03 micron. La loro presenza è alquanto rara poichè anche per livelli molto bassi di umidita' si trasformano in grossi ioni.
- GRANDI
Sono chiamati anche ioni di LANGEVIN, hanno una mobilità relativamente bassa e, come gli ioni intermedi non hanno praticamente effetto sulla conducibilità' elettrica dell' aria.
Molto spesso su di essi condensa il vapore acqueo formando i cosiddetti nuclei di condensazione.
L'IMPORTANZA DELLA IONIZZAZIONE DELL' ARIA.
Cap. 4
L'analisi bioclimatologica delle attività' umane considera come strutture ambientali sia quelle Interne che quelle esterne ( endosferiche ) ; Infatti deve sempre essere tenuto in considerazione che il microclima confinato è ugualmente soggetto alla Influenza ( positiva o negativa ) dell'ambiente spaziale esterno : temperatura , umidità , pressione, Ionizzazione, raggi cosmici.
Premesso questo , risulta facile sottolineare come lo studio del sistema , inteso come microclima circoscritto in cui l'uomo vive, comprende un numero di variabili tale che risulta molto complesso individuare con precisione gli effetti e le interazioni di ogni singolo parametro.
Non dobbiamo infatti dimenticare che le interazioni tra i composti inquinanti e i pararnetri climatologici hanno effetti sinergici.
Il grado di ionizzazione dell'aria dipende da fattori meteorologici , climatologici ed ambientali ; in condizioni naturali esiste un rapporto di circa 1 : 1.2 tra le cariche elettriche negative e quelle positive.
La concentrazione degli ioni gassosi presenti nell' aria tende a diminuire in presenza di inquinamento ; in particolar modo per quanto riguarda 1' inquinamento dell' aria all'interno degli spazi abitati e' indispensabile mettere in evidenza come i condizionatori d' aria, gli impianti di riscaldamento, il fumo di sigarette, terminali video ed altre apparecchiature elettriche usate in casa o negli ambienti di lavoro riducano drasticamente la concentrazione degli aeroioni negativi.
Oggi vi sono moltissime ricerche condotte con stretto rigore scientifico e supportate da Istituti ed Enti nazionali ed internazionali che dimostrano con estrema evidenza come la carica elettrica dell' aria , riferita alla presenza di piccoli aeroioni eserciti un' influenza tutt'altro che trascurabile.
Naturalmente il presupposto d' analisi deve essere puramente scientifico e non lucroso ; ogni giorno siamo infatti bombardati da false informazioni pubblicate su giornali e riviste da produttori poco seri che attribuiscono agli ioni negativi effetti miracolosi, e' necessario sempre valutare attentamente e prendere in considerazione solo le informazioni corredate di dimostrazione scientifica.
Il Prof. Kruger ( Biomedicai Laboratory Science Division and Naval Biological Laboratory , University of California U.S.A.' ha dimostrato che gli aeroioni negativi provocano una diminuzione del tasso di 5-HT ( serotonina ) , ed incrementano l'attività' ciliare sulla mucosa tracheale ; Gli aeroioni positivi invece agiscono in senso opposto.
Gli effetti benefici che gli aeroioni negativi esercitano sull'uomo sono molteplici , tuttavia dato il contesto della nostra valutazione analizzeremo il problema da un punto di vista strettamente tecnico.
Il prof. Alfredo MURRI ( fondatore dell'Osservatorio Geofisico Sperimentale di Macerata ) ha dimostrato in lunghi anni di ricerche in campo elettro-meteorologico e ciimatologico che alla predominanza della carica positiva dell'aria e' sempre associabile la presenza di un agente inquinante :
dalle sue ricerche infatti emerge chiaramente che umidità, polvere , gas di combustione, abbassano la conducibilità' elettrica dell'aria ed associano ad essa una carica positiva che tende a ridurre sensibilmente il contributo delle cariche negative.
Questo problema assume notevole importanza soprattutto nello studio della qualità dell' aria all'interno delle abitazioni dove la presenza della polvere , di gas provenienti da combustioni ,di apparecchiature elettriche , di impianti di condizionamento e di riscaldamento, e la presenza di persone crea degli squilibri senz' altro non trascurabili .
Per quanto riguarda gli impianti di condizionamento dell'aria il problema che si pone assume dimensioni notevoli.
Infatti oltre agli effetti negativi che tutti conoscono devono essere tenuti in considerazione anche altri aspetti legati alle strutture stesse degli impianti :
1'aria che fluisce all'interno delle condotte di aspirazione ( metalliche ) viene privata delle cariche negative che dotate di maggiore mobilità si scaricano verso terra più facilmente che non le cariche positive.
Quindi 1' aria di un ambiente in cui è installato un condizionatore risulta impoverita della sua naturale carica elettrica e presenterà un eccesso di aeroioni positivi.
Da alcune ricerche condotte in edifici con impianti a ricircolazione d ' aria , è emerso inoltre che in questi casi l'ambiente e' praticamente deionizzato.
Se teniamo conto infine degli altri fattori (sopracitati) che all'interno delle abitazioni intervengono nella distruzione dei piccoli aeroioni ci rendiamo subito conto che il problema non può' essere trascurato, soprattutto nel momento in cui si effettua un' analisi delle condizioni microclimatiche ambientali.
DIAGNOSI E SUCCESSIVO INTERVENTO DI BONIFICA
Cap. 5
Le procedure tecniche che devono essere seguite in un' analisi della salubrità ambientale di un microclima circoscritto prevedono la misura di tutti i parametri che , come già detto , condizionano l'ambiente stesso .
Nel contesto della nostra valutazione prendiamo in esame le correlazioni tra la concentrazione degli aeroioni e 1'inquinamento dell'aria da microorganismi, composti organici volatili ( VOC ), particolato, pollini , ecc .
Innanzitutto e' necessario specificare che installare un purificatore d'aria dotato di dispositivi ionizzatori, non implica necessariamente aver risolto tutti i problemi di inquinamento e di comfort abitativo.
Tuttavia i risultati che si ottengono sono senz'altro apprezzabili e comunque , anche se non sollevano dalla necessità di eliminare tutte le cause di insalubrità' ambientale costituiscono in ogni caso un valido presupposto di risanamento.
La soluzione più' idonea , che quindi porterebbe i maggiori benefici, è l' impianto di ionizzazione e depurazione integrato nelle strutture dell' edifcio ; purtroppo le conoscenze degli addetti ai lavori nei riguardi di questo tipo di depurazione dell'aria sono ancora lontane per consentire questo tipo di progettazione.
Parleremo quindi di apparecchi da installare come ausilio di bonifica in case , uffici , ospedali ecc.
STRUMENTI E METODI
Cap. 6
Per la misura della Ionizzazione dell' aria si Impiega un misuratore di carica spaziale, in cui la mobilita' limite degli aeroioni che si Intende misurare sia corrispondente a quella del piccoli aeroioni ( K= 0.85 Cm 2 / V*Sec ).
Nel nostro caso abbiamo utilizzato lo ION-METER PN 2001 di fabbricazione PERISO ; uno strumento in grado di rilevare anche la singola carica elettronica con un campo di misura da O a 400 milioni di Ioni / Cm3 e con una risoluzione di 1000 ioni su 2.5 milioni.
Gestito da un microprocessore , svolge autonomamente tutte le funzioni di azzeramento , start , stop , adeguamento scale e se collegato con un PC esterno consente l'elaborazione immediata del dati raccolti.
Date le dimensioni ridotte si presta facilmente per misure in ambienti interni , dove può anche essere posizionato su un carrello rack che raccoglie altri strumenti atti a rilevazioni di parametri ambientali.
Per la misura dei microorganismi si utilizza un apposito campionatore d'aria a volumi programmabili , all'interno del quale vengono di volta in volta inserite delle piastre di Petri con i terreni di coltura sui cui avverrà lo sviluppo.
Per gli altri parametri invece si utilizzano gli strumenti che facilmente si trovano in commercio ( contatore di particelle, di nuclei di condensazione , di gas , ecc.) .
I dispositivi di depurazione dell'aria invece vengono scelti in relazione alla volumetria del locale da risanare e al tipo di attività' che accoglie ; essenzialmente si suole dividere le due categorie : civile ed industriale.
La costruzione degli apparecchi avviene con materiali sintetici ecologici , e cosi' pure per il filtro , che anche se incenerito non produce sostanza tossiche.
TECNICA DELLA DEPURAZIONE
Cap. 7
In linea generale si può sintetizzare il principio di funzionamento come segue :
gli apparecchi sono dotati di un silenzioso ventilatore tramite il quale avviene il riciclo forzato dell 'aria ; le particelle inquinanti presenti nell'aria ambiente caricata elettricamente dagli appositi dispositivi, vengono quindi catturate grazie alla doppia azione di forze coulombiane e d' induzione elettronica dalle fibre elettrizzate del filtro.
Il filtro , frutto di lunghe ricerche svolte alla 3M e' costituito da un prefiltro meccanico e dal filtro vero e proprio , composto da una moltitudine di fibre sintetiche elettrizzate e stabilizzate , in grado di trattenere il 95 % delle particelle aventi diametro 0.1 micron .
L'efficacia della depurazione di questi apparecchi e' insita nel concetto stesso di funzionamento ; infatti è grazie al fenomeno di ionizzazione degli agenti inquinanti che e' possibile eliminarli nella quasi totalità.
E ciò non solo nel caso di particolato e polvere ma anche , e soprattutto , nel caso di sostanze gassose, VOC.
Infatti sono state eseguite numerose ricerche , soprattutto in Germania , nei paesi del Nord Europa e in America con le quali si e' dimostrato l'efficacia della ionizzazione nell' abbattimento di sostanze gassose nocive alla salute (per esempio la Formaldeide, il 3,4 Benzopirene, gli Idrocarburi incombusti, il fumo di sigarette, gli ossidi di zolfo, di Carbonio, ecc.).
Per quanto riguarda invece la depurazione da microorganismi è di fondamentale importanza evidenziare l'assoluta efficacia degli aeroioni negativi : possiamo citare a questo proposito una ricerca ( ma ve ne sono molte altre condotte in molti altri paesi ) eseguita presso la Cllnica Mangiagalli di Milano :
In un locale di 200 m3 adibito a sala visite sono stati installati 4 dispositivi ionizzatori mod. ISO-ION NR 2. che garantivano un ricambio d'aria circa ogni ora.
Sono stati quindi rilevati i livelli di contaminazione batterica in due punti differenti utilizzando delle piastre di Petri a carica totale prima e dopo aver installato e messo in funzione i purificatori :
i risultati sono stati eccellenti , evidenziando la notevole capacita' di depurazione della ionizzazione negativa.
Infatti si può ' vedere molto chiaramente dal grafico riportato come , con il trascorrere del tempo , la concentrazione dei batteri diminuisce.
Dopo 24 ore di ionizzazione , si è verificata una diminuzione della carica batterica del 41% nel punto A e del 69% nel punto B.
Dopo una successiva ora di ionizzazione si e' verificata una ulteriore diminuzione della carica batterica del 62% nel punto A e del 42 % nel punto B
CONCLUSIONI
Cap. 8
A questo punto ci si rende conto con estrema chiarezza della importanza che riveste la ionizzazione negativa dell 'aria.
Correttamente impiegata, con apparecchiature idonee , sicure e garantite dal marchio di qualità e con un' attenta analisi della situazione climatologica, operata tramile appositi strumenti in grado di rilevare il livello della carica spaziale , è possibile ottenere risultati che, considerato il rapporto necessita'- costi -risultati non sono raggiungibili con altri sistemi o apparecchiature oggi in commercio.
E considerando 1'entità del problema costituito dall' inquinamento dell'aria negli ambienti interni , non si può fare a meno di notare come sia estremamente vantaggioso ed economico questo sistema di depurazione , che tra l'altro consente di eliminare alcuni inquinanti (per esempio la formaldeide ) contro i quali i sistemi oggi a disposizione sono , a volte , economicamente inaccettabili o , nella maggior parte dei casi , inattuabili.
E' comunque necessario stare in guardia dai produttori poco onesti che commercializzano apparecchiature prive di marchi di qualità e non sottoposte a severi controlli circa l'emissione di sostanze nocive : il dispositivo che da' origine al fenomeno fisico della ionizzazione dell'aria deve essere rigorosamente progettato seguendo e criiteri di assoluta sicurezza.
Infatti e' doveroso far notare che riprodurre artificialmente il fenomeno della ionizzazione dell'aria non e' cosi' semplice come si potrebbe pensare : si corre infatti il rischio di generare ozono oppure di ossidare l'azoto o altri gas presenti nell'aria peggiorando così la situazione tra l'altro già precaria.
In definitiva quindi possiamo concludere questa breve analisi considerando che quando si studiano i problemi degli ambienti di vita in relazione alla salute dei cittadini e' necessario prendere in considerazione tutti i parametri che intervengono , tra i quali quindi anche la ionizzazione dell' aria , fino ad oggi trascurata.
BIBLIOGRAFIA
ALBRECHTSEN ( 1979 ) : Thè effect of electric fleids in mental work.
CENSI - FUSARI - MURRI - SCUTERINI : Correlazioni fra parametri elettrici atmosferici ed alcuni fenomeni biologici.
A. MURRI " C. SCUTERINI : Ricerche sulla carica spaziale.
FRIGERIO - CALDARELLA - MOLTENI - GARLASCHI - ROSSI : Ionizzazione artificiale dell' aria e riduzione della carica batterica in una sala operatoria ginecologica.
HAWKINS - BARKER ( 1978 ) : Air lons and Human Performance.
HAWKINSON - BARBER ( 1981 ) : Thè industriai Hyglene significane e of small air lons.
JONASSEN ( 1985 ) : Thè physics of air ionisation.
KRUEGER " KOTAKA : Thè effect of air lons on experimental respiratory infections.
KRUEGER - BROOK » REED ( 1975 ) : Air lon Action on Bacterla. KRUEGER ( 1985 ) : Thè blological effect of air lons. LOMBARDO : L' elettroaerosolterapla dell' asma bronchiale*
MOESE - FISCHER : (1976 ) Research of Blological Effects of Electric Enviromental Factors.
SULMAN ( 1976 ) : Health . weather and climate.
SULMAN " LEVY - LUNKAN - PFEIFER " TAL. : Absence of Harmfui Effects of Protracted Negative Air Ionisation.
SVAB ( 1976 ) : lonizzatori per uso medico.
dizionario
ionizzazione
Con il termine ionizzazione si intende quel processo atto ad immettere nell'aria una certa quantità di ioni negativi, in modo da ristabilire i livelli di equilibrio che normalmente si trovano in natura.
Gli ioni negativi sono molto importanti e rappresentano un'incredibile risorsa per l'uomo: essi favoriscono la concentrazione, danno vitalità e benessere all'organismo.
Tra gli effetti benefici della ionizzazione dell′aria abbiamo:
• La normalizzazione della pressione arteriosa;
• La diminuzione della velocità di ossidazione dei globuli rossi;
• Il miglioramento dei processi respiratori dei tessuti;
• La normalizzazione dello scambio di vitamine (B1, B6, PP, C);
• L′aumento del livello di ossigeno nel sangue;
• L′aumento della capacità di termoregolazione;
• La normalizzazione del sistema cardiovascolare e motorio;
Il rapporto ottimale tra gli ioni dovrebbe essere di 3 ioni negativi per ogni ione positivo.
Purtroppo questo equilibrio viene spesso stravolto dall'attività umana che, con l'emissione di gas serra, polveri inquinanti, fumi e smili, può portare a volte il rapporto ad 1 contro 600, con conseguenze facilmente immaginabili sulla salute dell'individuo, causando, tra l'altro, spossatezza, asma, allergie e scarsa concentrazione.
Lo strumento che effettua l'azione di ionizzazione viene chiamato Ionizzatore
copyright © 2008 M.P. International S.r.l. - Gruppo Airone Italia
Con l'utilizzo di materiale ionizzante naturale trattato a livello nanotecnologico, disperso nei rivestimenti verniciati e plastiche, si possono ottenere buoni livelli di ionizzazione negativa, che vanno a compensare la presenza di ioni positivi(dannosi per la salute), portando il rapporto tra ioni molto favorevole alla condizione negativa, l'ipotesi migliore per classificare un ambiente in cui vivere.
European researchers investigated the risks of long-term exposure to traffic pollution in a study examining 5000 volunteers selected from the ongoing Netherlands Cohort study on Diet and Cancer (NLCS). They discovered that people living near major roads (and therefore exposed to higher levels of traffic-related air pollution) were more likely to die from cardiopulmonary disease or lung cancer than their rural peers, leading the authors to conclude that 'long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution may shorten life expectancy. (3)
Air Pollution Linked to Heart Damage
In addition to causing lung damage, air pollution is now also
recognized as a threat to cardiovascular health. Reporting in the March
6, 2002 Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA),
researchers examined long-term health data on 500,000 individuals to
compare increases in air pollution levels with incidence of death. They
discovered that when air pollution levels suddenly increased, in
addition to expected increases in deaths from asthma, pneumonia, and
emphysema, there was an unexpected increase in the number of deaths
related to heart attacks and stroke. Most surprising was the finding
that when air pollution levels rose, so did deaths from all causes, not
just those related to the heart and lungs (Fig. 1). (4)
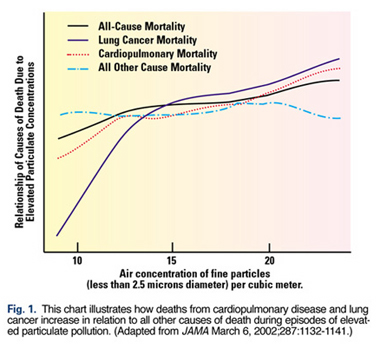 One possible explanation for the increase in cardiovascular-related
deaths is that air pollution causes oxidative stress that, in turn,
triggers an inflammatory response in the lungs that leads to the release
of chemicals that impair heart function and blood pressure.
One possible explanation for the increase in cardiovascular-related
deaths is that air pollution causes oxidative stress that, in turn,
triggers an inflammatory response in the lungs that leads to the release
of chemicals that impair heart function and blood pressure.
This was shown to be the case when scientists working in the Netherlands exposed rats to high levels of particulate air pollution. Following exposure, the researchers found that plasma levels of fibrinogen were elevated by 20 percent, which could presumably increase blood viscosity, leading to decreased tissue blood flow. They also measured a 400 percent jump in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and a 350 percent increase in nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in lung fluids. The researchers speculated that as particulates lodge in lung tissues they induce an increase in the production of nitric oxide (NO). Under normal conditions nitric oxide is an important neurotransmitter that aids numerous signaling pathways involved in motor learning, protein modification, arterial dilation and immune defense. But when conditions trigger the overproduction of NO as seen in the Netherlands study, the result is serious damage to the endothelial cells lining the blood vessels of the lungs. (5)
When Japanese researchers exposed guinea pigs to particulates from diesel exhaust, the lungs showed a significant elevation of leukotrienes and eosinophils, two important biomarkers of inflammation and cytotoxicity commonly observed in cases of chronic obstructive lung disease (COLD). The researchers noted that these findings indicate that chronic exposure to diesel exhaust induces continuous inflammation and overproduction of mucus and phospholipids in the lung. (6)
Another mechanism implicated in air pollution-related heart failures involves bone marrow and atherosclerotic plaques. Researchers in Vancouver, British Columbia found that exposure to high levels of air pollution stimulates bone marrow to release leukocytes and platelets that accumulate preferentially in pulmonary capillaries. In addition to causing damage to lung tissues, the researchers also observed that inhalation of particulate pollution causes changes in atherosclerotic plaque lesions that make the deposits more vulnerable to rupture.
They postulated that exposure to particulate air pollution induces a systemic inflammatory response that includes the release of inflammatory mediators that stimulate bone marrow to release leukocytes and platelets, leading to lung inflammation and changes of atherosclerotic plaque, making them more vulnerable to rupture. (7)
Diabetics and Elderly at Increased Risk
Diabetics are particularly susceptible to cardiovascular damage
caused by airborne pollution. A recent study published in the journal
Epidemiology examined Medicare records and hospital admissions in US
cities: Chicago, Detroit, Pittsburgh, and Seattle. Looking at records
from 1988 to 1994 they found that diabetics were twice as likely as
non-diabetics to be admitted to a hospital with a cardiovascular problem
caused by airborne particulate pollution. They also found that persons
75 years of age and older also faced a higher risk of cardiovascular
injury. (8)
Children and Air Pollution
Children are particularly at risk for health issues related to air
pollution. Chronic exposure to particulates, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen
dioxide have been associated with up to 300 percent increases in
nonspecific chronic respiratory symptoms. Exposure to automotive
pollution, particularly from truck and diesel exhaust, has been shown to
cause significant increases in respiratory symptoms and decreased lung
function. (9)
To examine the relationship between traffic-related air pollution and childhood development of asthma and other childhood respiratory diseases and infections, researchers in the Netherlands looked at data from some 4,000 babies born in the Netherlands. The health of the children was linked to measurements of traffic-generated air pollution (nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter less than 2.5 microns in diameter, and soot) in the homes of each subject. Their study found that, by the age of two years, children exposed to higher levels of air pollutants were more likely to suffer from wheezing, physician-diagnosed asthma, ear/nose/throat infections, and flu/serious colds. (10)
Part of the problem for children is that studies show that – relative to their size – children inhale more deeply and trap more airborne particles and pollutants in their lungs than either adolescents or adults. (11) Children also have higher metabolic rates than adults, breathe more than adults, and spend more time outdoors than adults, exacerbating their susceptibility to pollution-related health problems.
Children's Growth Stunted
When Polish researchers examined the effects of air pollution in
Krakow they discovered that children living in those areas with the
highest levels of air pollution suffered from stunted growth. After
collecting data on 958 children and assessing body growth rates by
height changes they found that body growth rates for children from the
most highly polluted area was lower by 1.5 cm over a 2-year period than
those from the control area. The compromising effect of air pollution on
height gains was about the same for both short and tall children. (12)
Air Pollution and DNA Mutations
New research shows that the health threat posed by air pollution
may actually affect children even before they are born. On December 9,
2002, Canadian researchers published a study revealing that animals
exposed to polluted air close to a steel mill suffered genetic damage
and produced fewer offspring. Most alarming was the discovery that
damaged DNA was being passed on to offspring by their fathers. While
virtually all mutations were inherited from the father mice, the
researchers said this doesn't mean that females are not susceptible.
What it does suggest is that steel workers, who are mostly male, may be
at extra risk of similar damage.
Christopher Somers, James Quinn, and colleagues published an earlier study that found that gulls living near a steel mill on Lake Ontario suffered from genetic mutations. In a current study the researchers raised two groups of mice – the first a half-mile downwind of a steel mill on Lake Ontario, and the second about 20 miles away. The mice breathing the polluted air had twice as many mutations in their DNA as the mice breathing fresh country air. (13)
The findings suggest that steel mill workers and people living near those mills should be checked for damage to their health, said the researchers, at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario. "Our findings suggest that there is an urgent need to investigate the genetic consequences associated with exposure to chemical pollution through the inhalation of urban and industrial air."
Ironically, the study was originally aimed at showing how efforts to clean up pollution around the steel mill had improved the environment. 'This had been one of the most polluted places, if not the most polluted place in Canada,' stated Christopher Somers, one of the lead researchers. 'There has been a concerted effort to clean up Hamilton harbor and reduce air emissions.' The experiment had been aimed at showing these had helped. ''We haven't really seen that,'' he said.
Protecting Your Lungs
While government, business and environmental interests wrangle over
a morass of economic, legislative and technological solutions for
cleaning up polluted air, the vital issue facing individuals is how best
to protect their health. Currently over 75 million people in the US
live in counties where the air concentrations of particulate matter
smaller than 2.5 microns (PM2.5) exceed safe levels (Fig. 2.). (14)
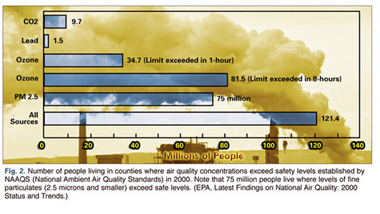
Air Purifiers
As the scope of air pollution related health problems grows, so too
does the number of people turning to air purifying solutions for
protection. Home air filtration products offer a number of options,
including electrostatic, UV radiation, water and advanced HEPA
filtration technologies. Until recently, these products – many
engineered for entire houses and buildings – were bulky and expensive to
install and maintain, placing them out of reach for most people.
Recently, a number of consumer products have become available utilizing
ion-generating technology to eliminate airborne pollutants, allergens
and viruses from immediate breathing spaces.
These devices work by generating a flow of negative ions that charge and bind together airborne particulate matter, which then clumps and precipitates out of the air. Ion generating devices have been shown to be effective against dust, cigarette smoke, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, viruses, and bacteria. In addition to eliminating harmful particulates from the air, negative ions also have a number of unique health benefits.
Scientific evidence began to mount in the 1970s when researchers measured metabolic changes in mice and rats in response to changes in ion charge (negative or positive) and concentration, including alterations in serotonin levels and recovery from illness. When exposed to positive ions (which accumulate in the atmosphere at the beginning of a storm) researchers routinely noted that animals became agitated, aggressive and were more prone to respiratory illness. Furthermore, when mice were infected with influenza virus and housed in an environment depleted of all ions, death rates increased, indicating a previously unknown benefit on overall health. (19)
Later, researchers measured the impact of atmospheric electricity on human subjects by monitoring daily changes in urine excretion of neurohormones in samples gathered from 1,000 volunteers exposed to positive ions generated 1 to 2 days prior to the arrival of a storm front. By measuring the changing levels of neurohormones in the 24-hour urinary output of the subjects during normal and weather-stress days, the researchers compiled a profile of changes in levels of serotonin, 5-HIAA (5-hydroxyindole acetic acid, a serotonin metabolite), adrenaline, noradrenaline, histamine and thyroxine.
The researchers found that the electrical charges (positive ionization) engendered by every incoming weather front produce a release of serotonin. (20) They further identified three classes of weather sensitivity reactions:
Further evidence of the influence of ions appeared when scientists exposed mice to an atmosphere enriched with either positive or negative ions. While negative ions had no negative effect on the mice, positive ions caused elevations in norepinephrine levels within one day. When exposure to positive ions was continued for longer periods, ranging from 3 to 10 days, norepinephrine levels dropped. The author noted that the results showed that "positive ions cause stress after short time application in excess. After longer exposure, a state of exhaustion can be observed in the form of a lowered norepinephrine level." (22)
Health Benefits of Negative Ions
Just as positive ions build up in the atmosphere prior to a storm
front, negative ions accumulate following a storm. This surfeit of
negative ions has long been associated with improvements in mood and
physical health. Research conducted in the last decade has begun to
support the view that negative ions have a net positive effect on
health.
One of the most tantalizing hints regarding negative ions and health surfaced when German researchers discovered a link between catecholamine regulation and lifespan after depriving experimental animals of negative ions. First, researchers at the Goldstein and Lewin Dept. of Medical Research in Stahnsdorf, Germany isolated mice and rats in air-tight, sealed acrylic cases. Next, they filtered the ambient air to remove all negative ions from the sealed cases. Their research led to the discovery that a prolonged deficiency of negative ions led to an accelerated rate of death for the experimental animals. Examination of the animals led researchers to conclude that the results 'strongly suggest that animal death is related to disturbances in neurohormonal regulation and pituitary insufficiency. (23)
Researchers at the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow discovered that negative ions are able to help protect the body from induced physical stress. When the researchers immobilized rats and exposed them to negatively charged air ions they discovered that the ions prevented the development of pathological changes characteristic of acute stress that are observed in untreated rats. The protective action of negative air ions was observed in all the experimental animals independently of their types of behavior. (24)
British researchers at the Centre for Sport and Exercise Sciences in Liverpool exposed male subjects to negative ions and measured physiological responses, including body temperature, heart rate and respiration, while at rest and during exercise. Negative ions were found to significantly improve all physiological states, particularly during rest. Most important was the finding that negative ions are "biologically active and that they do affect the body's circadian rhythmicity." (25)
Another clue to the role of negative ions in health comes from Russian research conducted at the Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Biophysics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, in Pushchino, Russia. Researchers found that exposure to negative ions increased levels of the protective antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) in mammalian erythrocytes. The researchers also discovered minute amounts of H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide), writing, "The primary physiochemical mechanism of beneficial biological action of negative air ions is suggested to be related to the stimulation of superoxide dismutase activity by micromolar concentrations of H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide)." (26)
Summary
While progress has been made in some areas of air pollution, such
as reductions in emissions of lead, sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen
dioxide (NO2) and ozone (O3), air pollution, particularly from
particulates, remains a serious health problem. In addition to damaging
the lungs and heart, air pollution is now recognized as being especially
harmful to children, the elderly, and select sensitive populations,
such as those afflicted with diabetes, cardiopulmonary diseases and
other debilitating illnesses.
To address air pollution-related health problems a growing number of people are using personal and home air filtration products that generate negative ions to charge and precipitate airborne particulate matter for removal to create localized zones of improved air quality.
Consumer devices that utilize negative ion-generating technology have been shown to eliminate airborne pollutants, dust, cigarette smoke, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, viruses, and bacteria from the air. Negative ions have long been attributed to improvements in mood and physical health. Research supports the view that negative ions have a net positive effect on health, including improved mood, stabilized catecholamine regulation and circadian rhythm, enhanced recovery from physical exertion and protection from positive ion-related stress and exhaustion disorders.
References
1. Vrang ML, Hertel O, Palmgren F, Wahlin P, Raaschou-Nielsen O,
Loft SH. Effects of traffic-generated ultrafine particles on health.
Ugeskr Laeger 2002 Aug 19;164(34):3937-41.
2. Polosa R, Salvi S, Di Maria GU. Allergic susceptibility associated with diesel exhaust particle exposure: clear as mud. Arch Environ Health 2002 May-Jun;57(3):188-93.
3. Hoek G, Brunekreef B, Goldbohm S, Fischer P, van den Brandt PA.Association between mortality and indicators of traffic-related air pollution in the Netherlands: a cohort study. Lancet. 2002 Oct 19;360(9341):1184-5.
4. JAMA March 6, 2002;287:1132-1141.
5. Ulrich MM, Alink GM, Kumarathasan P, Vincent R, Boere AJ, Cassee FR.. Health effects and time course of particulate matter on the cardiopulmonary system in rats with lung inflammation. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2002 Oct 25;65(20):1571-95.
6. Ishihara Y, Kagawa J. Dose-response assessment and effect of particles in guinea pigs exposed chronically to diesel exhaust: analysis of various biological markers in pulmonary alveolar lavage fluid and circulating blood. Inhal Toxicol 2002 Oct;14(10):1049-67.
7. van Eeden SF, Hogg JC. Systemic inflammatory response induced by particulate matter air pollution: the importance of bone-marrow stimulation. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2002 Oct 25;65(20):1597-613.
8. Zanobetti A, Schwartz J. Cardiovascular damage by airborne particles: are diabetics more susceptible? Epidemiology 2002 Sep;13(5):588-92.
9. Nicolai T. Environmental air pollution and lung disease in children. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 1999 Dec;54(6):475-8.
10. Brauer M, Hoek G, Van Vliet P, et al. Air pollution from traffic and the development of respiratory infections and asthmatic and allergic symptoms in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002 Oct 15;166(8):1092-8.
11. Inhalation Toxicology, Sept. 1998;10:831-842.
12. Jedrychowski W, Maugeri U, Jedrychowska-Bianchi I. Body growth rate in preadolescent children and outdoor air quality. Environ Res 2002 Sep;90(1):12-20.
13. Christopher M. Somers, Carole L. Yaukdagger, Paul A. Whitedagger, et. al.. Air pollution induces heritable DNA mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, Vol. 99, Issue 25, 15904-15907, December 10, 2002.
14. EPA, Latest Findings on National Air Quality: 2000 Status and Trends.
15. Smog Check II for All. San Jose Mercury News, Sep. 29, 2002.
16. R.B. Mosley, D.J. Greenwell, L.E. Sparks, Z. Guo, W.G. Tucker, R. Fortmann, C. Whitfield. Penetration of Ambient Fine Particles into the Indoor Environment. Aerosol Science and Technology: Vol. 34, Num. 1; Jan. 2001.
17. J. Thornburg, D.S. Ensor, C.E. Rodes, P.A. Lawless, L.E. Sparks, and R.B. Mosley. Penetration of Particles into Buildings and Associated Physical Factors, Part I: Model Development and Computer Simulations. Aerosol Science and Technology: Vol. 34, Num. 3; March 2001.
18. Sulman FG. The impact of weather on human health. Rev Environ Health 1984;4(2):83-119.
19. Krueger AP, Reed EJ.Biological impact of small air ions. Science 1976 Sep 24;193(4259):1209-13.
20. Sulman FG. Migraine and headache due to weather and allied causes and its specific treatment. Ups J Med Sci Suppl 1980;31:41-4.
21. Sulman FG, Levy D, Lunkan L, Pfeifer Y, Tal E. New methods in the treatment of weather sensitivity. Fortschr Med 1977 Mar 17;95(11):746-52.
22. Udermann H, Fischer G. Studies on the influence of positive or negative small ions on the catechol amine content in the brain of the mouse following shorttime or prolonged exposure. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg [B] 1982 Apr;176(1):72-8.
23. Goldstein N, Arshavskaya TV. Is atmospheric superoxide vitally necessary? Accelerated death of animals in a quasi-neutral electric atmosphere. Z Naturforsch [C] 1997 May-Jun;52(5-6):396-404.
24. Livanova LM, Levshina IP, Nozdracheva LV, Elbakidze MG, Airapetiants MG. The protective action of negative air ions in acute stress in rats with different typological behavioral characteristics. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 1998 May-Jun;48(3):554-7.
25. Reilly T, Stevenson IC. An investigation of the effects of negative air ions on responses to submaximal exercise at different times of day. J Hum Ergol (Tokyo) 1993 Jun;22(1):1-9.
26. Kosenko EA, Kaminsky YuG, Stavrovskaya IG, Sirota TV, Kondrashova MN. The stimulatory effect of negative air ions and hydrogen peroxide on the activity of superoxide dismutase. FEBS Lett 1997 Jun 30;410(2-3):309-12.
In situations where dust may carry microorganisms, negative air ionization can be economical to use to reduce infections. It has been used economically to reduce the incidence of Newcastle Disease Virus in poultry houses (Mitchell 1994). Poultry houses can be notoriously dusty.
 The above chart shows the Colony Forming Units (CFU) measured with
and without ionization in a dental clinic by Gabbay et al (1990).
Airborne microbial levels were reduced by 32-52% with ionization. He
also found that horizontal plates picked up considerably more cultures
than vertical plates, strongly suggesting that settling out of ionized
particles was the primary mode of removal.
The above chart shows the Colony Forming Units (CFU) measured with
and without ionization in a dental clinic by Gabbay et al (1990).
Airborne microbial levels were reduced by 32-52% with ionization. He
also found that horizontal plates picked up considerably more cultures
than vertical plates, strongly suggesting that settling out of ionized
particles was the primary mode of removal.
 This chart summarizes the results of studies by Makela et al (1979),
who found that bacterial aerosols in patient rooms of a burns and
plastic surgery unit could be reduced with air ionization. Variations in
the bacterial levels were associated with bed-changing and other room
activities. The humidity in the rooms was low, which may have enhanced
the effect.
This chart summarizes the results of studies by Makela et al (1979),
who found that bacterial aerosols in patient rooms of a burns and
plastic surgery unit could be reduced with air ionization. Variations in
the bacterial levels were associated with bed-changing and other room
activities. The humidity in the rooms was low, which may have enhanced
the effect.
 In this chart, also based on results from Makela et al (1979),
specifically identified Staphylococcus aureus levels in a room with and
without ionization. The average for two days of monitoring indicated a
definitive reduction in airborne levels. Staphylococcus aureus is a
potential nosocomial infectious agent of wounds and burns.
In this chart, also based on results from Makela et al (1979),
specifically identified Staphylococcus aureus levels in a room with and
without ionization. The average for two days of monitoring indicated a
definitive reduction in airborne levels. Staphylococcus aureus is a
potential nosocomial infectious agent of wounds and burns.
 The chart above summarizes some results from Happ et al (1966), who
found that levels of aerosolized virus T1 bacteriophage were rduced
under various types of ionization, which included mixed ions, negative
ions and positive ions. All three types of ionization had comparable
results in terms of reducing airborne levels. The method used by Happ
involved testing the filtration efficiency, in which lower filter
efficiencies demonstrated lower recoveries rom the air. These lower
recoveries suggested either that the phage was not present in the air or
had perhaps been inactivated.
The chart above summarizes some results from Happ et al (1966), who
found that levels of aerosolized virus T1 bacteriophage were rduced
under various types of ionization, which included mixed ions, negative
ions and positive ions. All three types of ionization had comparable
results in terms of reducing airborne levels. The method used by Happ
involved testing the filtration efficiency, in which lower filter
efficiencies demonstrated lower recoveries rom the air. These lower
recoveries suggested either that the phage was not present in the air or
had perhaps been inactivated.
References
Asthma and Ions
Advanced Research on Atmospheric Ions and Respiratory Problems
by Guy Cramer
Sept. 2,1996
Ions are small particles that take on an electrical charge. In nature we tend to find between a few hundred to a few thousand of these ions per cubic centimeter. The small particles that take on this charge are either negatively charged, positively charged or neutral. In a cubic centimeter of air out over a grass field, we find the ratio is almost balanced between negative ions and positive ions. In other words we are breathing quantities of electricity.
Positive ions are known to make asthma victims worse. Positive ion winds such as the Chinook Wind in Calgary, Alta., Canada and the Santa Ana Winds in Southern California are known to coincide with Asthma attacks. There are many areas around the would known for positive ion winds (times when the ion balance has more positive ions per cubic centimeter than negative ions).
A Doctor treating burn victims with negative ion generators found that those patients who also had respiratory problems - chronic bronchitis or asthma - all reported that negative ion therapy helped them breath more easily. With these findings the Doctor started research into the effects of ions on respiratory ills. This research was carried out at the Northeastern Hospital, at the University of Pennsylvania's Graduate Hospital, and the Frankford Hospital in Philadelphia. He found 63% of patients suffering from hay fever or bronchial asthma "have experienced partial or total relief" because of negative ion therapy. One hospital doctor who worked on the project said later, " They come in sneezing, eyes watering, nose itching, worn out from lack of sleep, so miserable they can hardly walk. Fifteen minutes in front of the negative ion machine and they feel so much better they don't even want to leave."
In Britain two Oxford University statisticians conducted a study among 100 victims of asthma, bronchitis, and hay fever chosen at random from a list of people who had purchased negative ion generators in the hope that it would help their problems. In the end their report was based on interviews with only 74 of the 100. They found that 18 of 24 asthmatics; 13 of 17 bronchitis sufferers; 11 of 12 hay fever victims; and 6 of 10 people afflicted with nasal catarrh reported that negative ion generators had noticeably improved their condition. A few claimed the generator had cured them.
Brazilian Hospitals have commonly used ionizing devices for the treatment of breathing problems, including allergies, following a test involving 36 children with asthmatic allergies. All of them had consistent and in some cases crippling problems before taking negative ion therapy; during the treatment only one of them suffered an allergy attack and afterward all were reportedly cured, at least to the point that they no longer suffered problems so long as they took part in occasional negative ion therapy sessions.
In 1966 at a hospital in Jerusalem, doctors performed a series of tests on thirty- eight infants between two and twelve months old. All suffered to about the same degree from respiratory problems. They were divided into two groups of nineteen, one kept as a control group in a ward without any ion charge and the other where a negative ion generator was in use.
The researchers reported that negative ions without any other treatment - that is, no drugs - seemed to cure attacks of asthma and bronchitis more quickly than drugs, antibiotics included. They also observed that there were none of the "adverse side effects" frequently found when treating such children with drugs. They concluded that the children treated with negative ions were less prone to "rebound attacks" (relapses). As to objectivity, the scientific report said that the tests "demonstrated that the atmospheric ions have an effect on infants, especially those suffering from asthmatic bronchitis." Less scientifically, they found that babies didn't cry as often and as loudly when they were breathing negative ions as they did in normal air. And there is nothing subjective about a bawling baby.

Humidity and Asthma
In humid areas - New York in high summer, for instance, or in Toronto - part of the familiar discomfort is caused by the fact that air becomes ion-depleted. Really humid days are murder for anyone suffering from asthma or any respiratory allergy, and the fact that such people find it difficult to breath in hot, humid air may have less to do with the amount of oxygen in the air then with the massive negative ion depletion. Air electricity is quickly conducted to the ground by the moisture in the air, and what negative ions there are attach themselves to particles of moisture and dust and lose their charge. We have seen how positive ions make breathing more difficult and reduce the body's ability to absorb oxygen; and how negative ions help breathing and improve oxygen absorption. (*NOTE; DO NOT USE HUMIDIFIERS OR VAPORIZERS WITH NEGATIVE ION GENERATORS. NEGATIVE IONS WILL ATTACH TO WATER MOLECULES FROM THE HUMIDIFIER OR VAPORIZER AND CREATE POSITIVE IONS. OUR OWN STUDIES HAVE SHOWN THIS EFFECT.)

Pollen, Pollution and Asthma
The ion count is always low in cities where there's precious little open ground to generate them. Pollution makes a bad situation worse, since it tends to deplete the negative ion count even more. The high pollen count in certain parts of North America each fall cuts even further into the negative ion count, since pollen has the same effect as dust. The end result is that the total ion count in cities is always down to what many scientists consider perilously low levels. As if that weren't bad enough, the normal 5 - 4 ratio of positive ions to negative ions is distorted so that people are, in a sense, victims of positive ion poisoning.

Central Air Conditioning and Heating
Hot or cool air forced through the duct work of most central heating and air- conditioning systems sets up friction that results in the loss of almost all the negative ions and also draws most of the positive ions out of the air as well. Then comes the coup-de-grace: This air with some positive and virtually no negative ions is forced out through vents in to rooms, offices and passages - and as it passes through the vents more friction is set up that generates an additional overload of positive ions. What finally comes out of most heating or air- conditioning outlets in the offices we work in and the rooms we live in is likely to be an overload of positive ions which will upset the mental and physical equilibrium of everyone, not only those of us who are ion sensitive.
Just how bad these systems are depends to a great extent on their design and the material from which the duct work is made. The design or layout of the whole system is crucial. At bends and curves and right-angle junctions the friction between ducts and air increases and has the effect of increasing the number of positive ions in the air. What comes out of the heating and cooling vents in any centrally heated or air-conditioned building is air that is not only low in total ions, but also has a heavy positive ion count when measured against the almost negligible quantity of negative ions. It is because of the design of this duct work that some parts of a building may be more "uncomfortable" to work in then others. That depends on whether you're on the receiving end of air that has passed a particular section of duct work, where there is a sharp bend near the outlet - as the air is forced around bends and corners there is greater friction and a consequent increase in positive ions.

Asthma and Synthetics
Asthmatics or people with emphysema and other respiratory ills often suffer additional agonies because of the cloth they wear, and are just as often unaware of the reason why they suffer. Dr. Bernard Watson, professor of medical electronics at Britain's St. Bartholomew's Teaching Hospital in London, says: "Changing the immediate unhealthy ion environment to help asthmatic means changing everything, clothes, sheets, furniture - just everything." One of his patients a girl at that time of fourteen, who had begun to suffer from serve migraine because of clothing - and then cured it herself. When she grew to adolescence and began to wear, with great pride, nylon bras and panties favored by most women, she began to suffer from occasional headaches for the first time in her life. When she graduated to slips and night-dresses and pretty nylon blouses, she became a full-fledged migraine sufferer. Her local general practitioner could offer neither explanation nor help beyond suggesting the onset of menstruation as a cause. But the girl was bright enough to associate the clothes of blooming womanhood with her problem and promptly abandoned the feminine underwear and nightdresses. Now her clothes are of cotton, which is the only fiber that creates no charge at all, and of natural fibers like wool, which carry little charge of either kind. However, once migraine has taken root it is not easy to cure and Dr. Watson is still treating the girl, in part by suggesting to her parents that certain items of furniture in their home should be removed.
The Director of the Danish Air Ionization Institute, Christian Bach (electrical engineer) has studied the clothes and environments of asthmatics and others who suffer from positive ion poisoning, then pinpoints the offending fabrics and articles that are throwing the ion effect out of balance. Bach and his colleagues have worked with many hospitals in treating many victims of asthma and other respiratory ills.
Bach tells of what has become a classic case history involving a woman who had asthma in her own apartment but not in the homes of friends. Even a negative ion generator was of no help, so Bach conducted what must have been one of the oddest investigations in history: Was the culprit the furniture, the television set, the bedding, the lamp shades? Bach found that the lady's taste ran mostly to modern synthetic fabrics. However, that alone was insufficient to explain the problem, so Back began cross-examining the woman about her housekeeping. He found that her furniture was treated with cellulose and silicone-based furniture finishes. Laboratory tests proved that such finishes, when rubbed with polishing rags and dusters, produce a positive charge. Then he visited the friends in whose home her asthma condition disappeared. There he found that the furniture was hand polished with old-fashioned wax and elbow grease, which produced no static charge at all. Bach coated the victim's furniture with an anti-static compound, told her to buy antique furniture without modern wood treatments, and her asthma attacks ceased.
In all, Bach had by 1967 treated almost 1,000 hay fever and asthma cases whose problems were cured or eased by his "passive therapy" approach. in one case, he says, a man became an asthma victim because his wife bought two new lampshades that led to overproduction of positive ions; In another instance several members of the same family became sufferers because their new television set had a teak cabinet that had been treated with cellulose. He also. He also tells of one instance in which he was called in to help save the fortunes of a chicken farmer. The farmer had two monstrous chicken houses each housing 20,000 chickens. In one of them between 150 and 200 chickens died every week. Bach found that both chicken houses were of identical design and construction, except that the one where the chickens died had a roof lined with sheets of plastic while the other had a roof lined of wood. Whenever there was a change in whether the death rate went up. Bach concluded that when the whether changes affected air electricity the plastic stimulated the production of positive ion overdoses. He treated the roof with anti-static substance, and within weeks the chicken mortality rate was normal in both hen coops.
Bach says like all Scandinavians, the Danes keep their homes spotless, forever flourishing dusters, wielding brooms, pushing vacuum cleaners, and otherwise raising clouds of dust to which negative ions are attracted, and so disappear as physiologically active small ions. It is it would seem, healthier to be a sloppy housecleaner then a meticulous one. At the International Ion Research Conference in Philadelphia in 1961. Dr. Hansell ended his speech by saying that to prevent a buildup of potentially harmful ions the person who comes home from work should promptly take his shoes off and walk around the carpets in their stocking feet. And he added, "My suggestion to the house cleaner is that it is very well known fact that it is very difficult to get a charge from a dirty surface. They should not, I suggest be too house proud."

Respiratory Tract and Ions
In the mid-1960s, Experiments showed that the cilia of the trachea, or windpipes, of small animals are stimulated by negative ions and depressed by positive ions. Human cilia, like those of small animals are microscopic hairs that maintain a whip like motion of about 100 beats per minute while cleaning the air we inhale of dust and pollen and other matter that should not reach the lungs. Subjected to tobacco smoke, which absorbs negative ions, the cilia slow down. Tobacco smoke plus positive ions make this slow-down take place from three to ten times more quickly than does smoke alone. An overdose of negative ions, however, neutralizes the effect of smoke on the cilia. Although this experiment took place in a laboratory and involved mice, rats, and rabbits, the implications are clear: Smoking and other forms pollution that absorb negative ions may also damage the ability of the cilia to clean the air that finally ends up in the lungs. Does that mean their is a relationship between positive ions and the incidence of lung cancer, particularly in smokers? As Bach points out, that is one of the many things about ionization we don't yet know, though scientists are investing the relationship.
The effect of ions on respiration is more obvious. The U.S. experimenters Windsor and Becket gave sixteen volunteer overdoses of positive ions for just 20 minutes at a time and all of them developed dry throats, husky voices, headaches, and itchy or obstructed noses. Five of the volunteers were tested for total breathing capacity, and it was found that a positive ion overdose reduced that capacity by 30 percent. Exposed to negative ions for ten minutes , the volunteers maximum breathing capacity was unaffected. What is significant here is that negative ions did not effect the amount of air breathed, but positive ions made breathing more difficult.

Negative ion generators (sold in North America as Air Purifiers / with negative ion generator). You should only have to pay between $50.00 - $250.00 for a negative ion generator depending on room size, (In certain areas medical covers some of these costs.). Bionaire sells these in Europe, Canada and the United States. they can be found at some Department stores and some drug stores. The plus for someone with respiratory difficulties is the added air purifier with carbon filters. The newer models have a hepa filtration system in them. Make sure you change the filters as directed in the instruction manual.
Negative ion generators are not a cure all. They do cause the body to convert excess serotonin (the antagonist for most of the problems) into a harmless chemical called 5HA ( 5-HIAA ).
If you do have respiratory difficulties and use a negative ion generator in your bedroom at night beware that the negative ion generator will keep you alert and awake longer then you might want. You may wish to only use the air filter at night. Most negative ion generators have an on/off switch for the ion control so you can use only the fan/filter system.
The majority of this report on Asthma and Ions was taken directly form the book;
"The Ion Effect" by Soyka, Fred ( Lester and Orpen Limited, 1977) these references can be found on pages 31, 35, 45, 56-57, 63, 75, 76, 77, 79-80, 84, 85, 90, 128, 129-131.
Special Olympic Report:
Secret Russian Sports Weapon Disclosed
 VANCOUVER, BC - September 21, 2000 (INB) -- Olympians may
benefit from technology derived from the Cold War Era. For decades the Russians
have been secretly using a unique performance enhancement device that has proven
to increase endurance levels by as much as 900%, balance coordination by 300%,
and
VANCOUVER, BC - September 21, 2000 (INB) -- Olympians may
benefit from technology derived from the Cold War Era. For decades the Russians
have been secretly using a unique performance enhancement device that has proven
to increase endurance levels by as much as 900%, balance coordination by 300%,
and reaction time by 100%. In studies conducted by the Soviet Union just after
World War II, negative ion generators were used during training of Track and
Field athletes, Gymnasts, Swimmers and Boxers, as part of a new Soviet policy
decision to dominate international sports.
reaction time by 100%. In studies conducted by the Soviet Union just after
World War II, negative ion generators were used during training of Track and
Field athletes, Gymnasts, Swimmers and Boxers, as part of a new Soviet policy
decision to dominate international sports.
Canadian ion scientist, Guy Cramer, has been studying the effects of ions on human behavior for 15 years. In this capacity, he has consulted for the NHL. In 1993 he confirmed that the Russians were still using these negative ion generators with the Russian Red Army and Olympic hockey teams as recently as 1989. This information was verified with former Russian hockey players now playing in the NHL. Naturally, Cramer was intrigued but not surprised by what he had discovered. He points out, "The Russians competed in their first international hockey tournament in 1958, only five years after the Czechs showed them how to play, and they won the world championship by beating the Canadians 7-2 in the final game. They literally skated our boys off their feet!" In the 1972 Summit Series between Canada and the Russians, Paul Henderson commented after the first game, "I worked really hard in training... by this time I was really gasping for air. And I look up and this Russian is standing beside me... not breathing at all... I just felt sick. I knew we'd been sucked in."
This may all sound a little far-fetched for the average sports fan, but the scientific community does recognize significant and measurable effects of ions on human behavior. An excess of positive ions produces detrimental effects both physically (headaches, dizziness, fatigue, circulatory disorders etc.) and mentally (irritation, apathy, anxiety, depression etc). Negative ions are beneficial, and can improve alertness, concentration and overall body function. These findings are based on research with air ions from groups and organizations such as Oxford University, RCA Laboratories, U.S. Air Force, Mercedes Benz, and the Swiss Bank... just to name a few of the more than 5000 studies. Negative ion generators/air purifiers are common household appliances found at many department and drug stores. The U.S. Navy uses these generators on the bridges of their ships to keep the command watch alert and energized.
Cramer's encyclopedic knowledge of ion-related information supports a rather suspicious theory. In his words, "The Americans discovered the Russian negative ion study in 1960, when U.S. intelligence translated the relevant documents (see abbreviated study notes attached). There is some anecdotal evidence that the U.S. may have used positive ions against the Russian Olympic hockey team during the 1980 Winter Olympics held in Lake Placid N.Y. They housed the Russians in a converted prison, and some of the key hockey players and the coach complained of symptoms that are associated with positive ion overdose. These positive ions would have taken away the advantage the Russians had built up training with negative ions. If the Americans used positive ions in the ventilation of the Russian accommodations to limit the Russians, then it is quite feasible that they could have used negative ions with their own U.S. team. The 1980 U.S. Olympic hockey team beat the Russians and went on to win the Gold Medal, which is now remembered as one of the biggest moments in sports history. Interesting, isn't it?"
The Olympic Committee knows about negative ion training, and has never objected to it, primarily because there are no known side effects and its considered natural, "If you trained within 1/2 a mile of Niagara Falls you would be training in high levels of negative ions. Negative ion generators simulate this effect," adds Cramer. Negative ion training certainly has not been widely embraced by athletic trainers, as most believed the Russian study to be propaganda until Cramer confirmed the ongoing undisclosed program recently. The Russians have been taking advantage of their "secret weapon" for years, and have many medals and world championships to show for it.
The Russians used the generators in relative secrecy, keeping the athletes in the dark. Many athletes knew about the generators but it was never disclosed to them what the generators were actually for. The research concluded that the athletes would retain the increased abilities for one month away from the system so they never had to bring it with them to competitions, tournaments or the Olympics.
Cramer tried to encourage the NHL to adopt the Russian system, but soon discovered a new perspective on 'enhanced performance.' "The General Managers were concerned that the improvement in athletic ability would translate into higher salary demands by the players, which current revenue streams could not justify. Needless to say, it's a bit disheartening when you have something that works too well," confides Cramer.
Cramer is now applying his scientific expertise to two entrepreneurial ventures, as a cofounder of HyperStealth Biotechnology Corp., http://www.hyperstealth.com, and United Dynamics Corp., http://www.superforce.com.
HyperStealth produces and markets a unique design of Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers, equipped with a proprietary Passive Negative Ion Generator, for which the company has patent pending. Cramer designed the passive generator after discovering distinct benefits in patient recovery when hyberbaric oxygen therapy was combined with negative ions. The passive negative ion generator is a lightweight unit which doesn't require a power source, that can also be clipped onto or sewn into clothing to combat fatigue and increase alertness, and is currently being tested with athletes, emergency workers and law enforcement officers.
United Dynamics operates a website, http://www.superforce.com, dedicated to forecasting the natural changing ion ratios in the atmosphere and correlating this data to various aspects of human behavior. With these forecasts, our Canadian scientist has been able to accurately predict trends in such activities as hockey and baseball games, golf tournaments, horse races and stock markets. In fact, phantom day trading experiments, ongoing for just over 9 months with certain indexes using his system have yielded remarkable results:
As a result of his work, Guy Cramer has recently been invited to appear on two major TV networks, including PBS's World Business Review hosted by Alexander Haig, and CNBC's DotCom hosted by Mark Hamill. Cramer's unconventional method has been featured in the Financial Post, one of Canada's leading national newspapers, in Grant's Investor, an online financial magazine Chaired by James Grant, the Vancouver Province Newspaper, on the MSNBC website, and is the subject of an article in the September issue of Ticker Magazine, a U.S. finance trade publication. The BBC Radio interviewed Cramer on the subject of the U.S. Presidential Election and the most optimum ion ratio day for voters to decide the fate of each candidate.
With the zero tolerance against banned substances so strictly and justifiably enforced by the Olympic Committee, perhaps it's time for more nations to take a closer look at ion training. With the inexpensive Passive Negative Ion Generator from HyperStealth and knowledge about the most favorable training days from http://www.superforce.com, Olympic Gold may be just a few extra breaths away.
Russian Ion-Athletics Study

The Following dials represent Real Time (Geomagnetic and Solar
Wind) data, which can override the Ion Ratio Forecast:
If the any of the dials move into the yellow, orange or red then there is a chance that positive ion ratios could be increasing and the stock market indexes are going up. If the dials remain in the green then the forecast applies. This page will auto-refresh every fifteen minutes to keep the dials up-to-date. If no arrows appear on each dial then the satellite is temporarily not receiving or transmitting data.
For detailed background information on the Ion Ratio Forecast visit the parent site United
Dynamics™ Corp.
La ionizzazione dell'aria è un parametro che acquista sempre maggiore importanza dal punto di vista ambientale, per gli effetti biologici che comporta e per la vasta gamma di applicazioni nelle più svariate discipline tecnico-scientifiche
(1). Il problema dell'esatta misura degli ioni atmosferici e di viva attualità poiché le metodiche portano a risultati non sempre concordanti (2). L'inquinamento elettrico ed elettromagnetico inducono azioni dannose sugli esseri viventi e sull’assetto biocenotico () di un Climax (), soprattutto attraverso variazioni della concentrazioni di ioni atmosferici (2). In defintiva il pullulare di linee elettriche, ripetitori, radiotrasmettitori, elettrodomestici, genera nello spazio una tale massa di cariche elettriche e magnetiche da determinare disturbi i più vari: astenia, cefalea, insonnia, nervosismo, sino a condizioni di estrema gravità. Anche se in disaccordo con vari organismi internazionali, alcuni ricercatori ritengono che le variazioni ioniche prodotte nell'ambiente dai campi elettrici e magnetici, possano modificare importanti sistemi di controllo omeostatico (ad esempio il rilascio di melatonina e di conseguenza sia il ritmo sonno-veglia che l'attività dei linfociti Natural Killer), ingenerando disturbi molto seri, prima funzionali ed infine anche organici (3).
Generando una sorta di "vento magnetico" essi risulterebbero in grado di cariche l'ambiente di ioni positivi, certamente dannosi per la salute umana, con ripercussioni sull'umore (riduzione della serotina e depressione) ed anche sull'equilibrio organico generale (accumulo di radicali liberi) (4). Intelligentemente la dott.ssa Comerio (5) ha già analizzato l’aggressione prodotta dai campi magnetici alla luce dei classici cinesi (Sowen e Shang Han Lun, soprattutto), ma il nostro scopo è quello di mostrare che le xie prodotte sotto forma di ioni e radicali, inducono una doppio "eccesso", contrassegnato da "Vento Esterno" e "Calore Interno" (con conseguente esuberanza di Yang e depauperamento progressivo di Yin, Jing e Sangue) (6-8).
Fin dagli anni settanta degli studi in lingua inglese hanno dimostrato che i campi elettrici e magnetici modificano il livello ed il tipo di ioni nell'ambiente circostante (9-10). Nella seconda metà degli anni settanta su Science (11) si è potuto dimostrare che esiste una precisa relazione fra morti per malattie cardiovascolari () e variazioni mensili d’elettromagnetismo. L'insieme dei dati sperimentali raccolti ci permette di affermare che i piccoli ioni negativi sono in grado di regolare al meglio i sistemi di controllo omeostatico, mentre gli ioni positivi producono variazioni di neurormoni e neurostrasmettitori (serotonina, noradrenalina, adrenalina) che inducono dapprima disturbi psicologici e poi malattie immunitarie o d’altro genere (12). Al pari dei "venti caldi"() che percorrono la terra e come le "macchie solari", i campi elettrici ed elettromagnetici caricano l'ambiente di ioni positivi producendo (per riduzione di catecolamine ed incrememento di 5-idrositriptamina) depressione, sonnolenza, apatia, cui seguono facilità alle infezioni, turbe immunitarie ed anche neoplasie (2,4,12).
Pertanto quello che potremmo definire "vento elettro-magnetico" induce una condizione di depauperamento progressivo, indipendentemente dai valori di produzione-distribuzione, di Energia Difensiva, con tutta una serie d’evidenti conseguenze per l'organismo. Prova diretta di questo è l'incremento del potere battericida dell'organismo se sottoposto all'azione di aeroionizzatori ad emissione di piccoli ioni negativi (13-14).
Di fronte ad individui i quali, senza altra causa apparente né congenita né acquisita (farmaci, HIV, diabete, ecc. ()) presentano riduzione d'efficienza immunitaria con vaghi disturbi neuropsichici (depressione, apatia, ecc.), si può presumere una quadro di eccessiva esposizione a campi magnetici a bassa frequenza (uso di telefonini, termocoperte, apparecchiature elettriche attive nelle camere da letto, ecc.).
Bibliografia
1. Nappi G., Maschicchi M.M., Calcaterra P., De Luca, De Luca S.: Studio sul parametro "ionizzazione dell'aria" nelle palestre dell'ISEF in Lombardia, Med. Clin. e Term., 1992, 18:43-50.
2. Marinelli F., Garcia A., Lozzio A., Valenzia V.I.: Clima e bioclimatologia marina: progressi e considerazioni sulla ionizzazione dell'aria e i campi elettromagnetici, materiale scientifico EURODREAM, La Spezia, 1999.
3. Iriki M.: Editorial, Journal of Biometereology, 1996, 1: 1-3.
4. Roberts G.F. & Anderson R.: La formula Everet Storey, Ed. Health Dimension, South-Oregon, 1999.
5. Comerio M. C.: Campi Elettromagnetici e salute umana, XX Congresso SIA, Firenze, 13-14 ottobre 2000, Atti.
6. De Berardinis D., Di Stanislao C., Corradin M., Brotzu R.: Organi e Visceri in Medicina Cinese, Ed. Sanli/Bimar, Roma, 1992.
7. Roustan C.: Traité d'Acupuncture, vol I, Ed. Masson, Paris, 1980.
8. Carnilot P. (Ed.): Acupuncture et Médicine Chinoise, Encyclopedie de Medicine Naturelle, Tome I, Ed. Techiniques, Paris, 1989.
9. Llaurado J.C., Sances A., Battocletti A.: Biological and Clinical Effects of Low-Frequency Magnetic and Electric Fields, Ed. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, 1974.
10. Soyka F. & Edmonds A.: The Ion Effects, Ed. Bantam, New York, 1977.
11. Kreuger A.P. & Reed J.: Biological Impact of Small Air Ions, Science, 1976, 193: 1209-1213.
12. Rosenthal N.E.: Winter Blues, National Institute of Mental Health, New York, 1990.
13. Gabbay J.: Effect of ionization on microbial air pollution in the dental clinic, Environ. Res., 1990, 52(1): 99-105.
14. Mitchell B.W.: Effect of negative air ionization and airborne trasmission of Newcastle disease Virus, Av. Dis., 1994, 38(4): 725-732.
note
Biocenotico è il complesso di organismi viventi presenti in un certo ambiente. Vedi:
- Soyka F.: Effects of ions, Ed. Lester and Open, Lichester, 1977.
- AAVV: Dizionario medico illustrato Dorland, Ed. Farmitalia-Sigma Tau, Milano-Roma, 1987.
Si definisce Climax l'equilibrio di organismi animali e vegetali posti nello stesso ambiente. Vedi: AAVV: Dizionario Medico, Ed. Zanichelli, Bologna, 2001.
L'infarto miocardico è definito "Vento del Cuore". Vedi: Ming O. (chef ed.): Chinese-English Dictionary of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ed. Joint Publication, Hong Kong, 1989.
Definiti con vari toponimi: lo scirocco in Italia, il maestrale in Francia, il foen in Svizzera, lo sharav in Medioriente, il northelies in Austria e i westerlies nel Nuovo Galles e nel Queensland, tutti in grado di provocare cicloneurosi con ansia, insonnia, depressione, nervosismo, tachicardia, ecc. Vedi
- Favilli U. (a cura di): Trattato di Patologia Generale, I Ed., Ed. Casa Editrice Ambrosiana, Milano, 1974.
- Lucchese M. (a cura di): Dizionario Medico Inglese-Italiano, Ed. Raffaello Cortina, Torino, 1986.
Si leggano:
- Lourencini da Silva R. , Albano F., Lopes dos Santos L.R. , Tavares A.D., Felzenszwalb I.:
The effect of electromagnetic field exposure on the formation of DNA lesions, Redox Rep., 2000, 5(5): 299-301.
- Pascual-Leone A., Walsh V., Rothwell J.: Transcranial magnetic stimulation in cognitive neuroscience--virtual lesion, chronometry, and functional connectivity, Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2000,10(2):232-237. 7
Vedi: Van Monttford J.C.: Immunotherapie, Ed. Ankh-Hermes, Deventer, 1990.
"La ionizzazione dell'aria nel controllo della IAQ"
Tra i parametri che influiscono sulla qualitàdell'aria negli ambienti chiusi, non va dimenticato il campo elettricoambientale determinato dagli ioni in sospensione. Mezzi artificiali possonopermettere di ristabilire un equilibrio ionico ottimale alterato
________________________________________
Il benessere di chi occupa uno spazio chiuso, come si sa, è uno stato soggettivo: non tutti siamo sensibili allo stesso modo al variare dei parametri ambientali come temperatura,umidità relativa, grado di pulizia dell'aria, illuminazione, rumore. Inoltre, certe condizioni particolari (umore, stress, attività,modo di vestire) possono influire pesantemente sulla personale condizione di benessere. Perciò, dato un certo ambiente, definito "confortevole"secondo tutti i normali parametri delle norme di buona progettazione ecostruzione, si troverà comunque una certa percentuale di persone che si sente a disagio. A volte, stranamente, questa percentuale diventa particolarmente elevata, molto superiore ai valori statisticamente attesi.Ciò significa che deve esserci un qualche altro parametro ambientale al quale gli esseri umani sono più o meno sensibili, parametro che normalmente non viene tenuto in considerazione in sede di norma e di progetto.Esistono numerosi indizi e qualche prova a carico di due importanti fattori ambientali:
• la ionizzazione dell'aria, intesa siacome quantità assoluta di ioni che come percentuale relativa tra ioni positivi e negativi;
• la presenza di campi elettromagnetici di varia frequenza ed intensità.
In particolare in questa sede ci si occuperà della ionizzazione dell'aria, sulla quale è possibile intervenire con mezzi relativamente semplici.
La ionizzazione naturale dell'aria
L'esistenza di un campo elettrico atmosferico divenne evidente per Benjamin Franklin un giorno del 1750, trascinando un aquilone tra le nubi nel bel mezzo di un temporale. In questo modo Franklin sperimentò anche l'effetto più imponente della ionizzazione atmosferica sull'organismo, la folgorazione. Una trentina d'anni più tardi, Bertholon si accorse che alcuni fenomeni atmosferici (i venti caldi phœn, sharav, scirocco) non solo erano causa di imponenti variazioni del campo elettrico dell'aria , ma parevano influenzare lo stato di salute delle persone. Nel 1899 Elster e Geitel dimostrarono per mezzo di sensibili elettroscopi la presenza nell'aria di particelle cariche positivamente e negativamente, di dimensioni molecolari, che vennero chiamate "ioni".Da allora in poi i lavori di numerosi ricercatori hanno permesso di chiarire la situazione elettrica dell'atmosfera (fondamentali i lavori di Langevin,1905).
Grossolanamente, le particelle elettricamente cariche che costituiscono il campo elettrico atmosferico sono le seguenti - fig.1
1. piccoli ioni leggeri; formati da molecoledi gas atmosferici che hanno perso (ioni positivi) o acquisito (ioni negativi)una o più cariche elettriche elementari (elettroni), per mezzo dell'azionedi fenomeni ionizzanti naturali, come i raggi cosmici, i raggi ultravioletti,la radioattività naturale. Caratterizzati da una elevata mobilità,sono preponderanti negli spazi aperti ed incontaminati;
2. grandi ioni pesanti; formati dalla agglutinazione di numerosi piccoli ioni sulla superficie di goccioline d'aerosol o di particelle solide. Sono tipicamente abbondanti nelle zone industrializzate ed affollate.
Numerosi lavori sperimentali hanno permesso di rilevare le concentrazioni ioniche presenti nei vari ambienti Tab.1,evidenziando le correlazioni tra situazione elettrica dell'atmosfera e stato di salute delle popolazioni esposte. In estrema sintesi, si può dire che la situazione ideale di benessere corrisponde ad una concentrazione ionica di 1800 piccoli ioni per cm3 d'aria, suddivisi tra positivie negativi con un rapporto di 0.8 a 1. Le sensazioni di disagio e di malessere sono invece correlate ad un eccesso di ioni positivi, come ad esempio accade in seguito a fenomeni meteorologici particolari, come la presenza di venti caldi ed asciutti (Scirocco, Fœhn, Sharav, nomi che la tradizione popolareda sempre associa a malanni fisici e psichici) oppure nell'imminenza di temporali (come ben sanno le persone cosiddette "meteoropatiche", particolarmente sensibili al peggioramento delle condizioni atmosferiche).
La ionizzazione dell'aria negli ambienti chiusi
Negli ambienti chiusi, la situazione ionica dell'aria è ben lontana dai valori ideali; infatti al chiuso sono preponderanti le fonti di ionizzazione positiva, mentre l'inquinamento indoor di origine organica ed inorganica porta alla formazione dei grossi ioni a discapito dei piccoli , che si trovano in quantità estremamente limitata. Nell'ambito della Indoor Air Quality, la ionizzazione dell'aria è un aspetto spesso dimenticato, oppure affrontato in modo improprio,con conseguenze non trascurabili. Nella maggior parte dei casi dove è presente un impianto canalizzato di trattamento dell'aria, questo stesso impianto è fonte di inconvenienti correlati alla ionizzazione dell'aria. Tutti conosciamo i caratteristici depositi nerastri in corrispondenza delle bocchette di diffusione dell'aria nell'ambiente: la loro presenza non solo è indice della presenza di particolato, ma è una conseguenza della ionizzazione dell'aria per frizione lungo le condotte, che provocala cessione della carica alle particelle in sospensione e la loro precipitazione. Per minimizzare questo fenomeno, è conveniente utilizzare condotte metalliche connesse all'impianto di messa a terra dell'edificio, assicurandola continuità elettrica tra sezioni diverse della canalizzazioneeventualmente isolate da guarnizioni per mezzo di collegamenti con trecciain rame o cavo elettrico di sezione adeguata. E' possibile inoltre intervenire installando, nel tratto di condotta in prossimità delle bocchette,speciali dispositivi in grado di eliminare le cariche elettrostatiche per mezzo di un campo elettrico alternato ad alta tensione, oppure generando una carica di segno opposto che neutralizzi l'eccesso di ionizzazione (lo sfregamento nelle canalizzazioni ionizza l'aria positivamente; quindi l'aggiunta di cariche negative ha un effetto neutralizzante). L'intervento più corretto e razionale consiste nell'installazione di filtri adeguati per bloccare il particolato, correggendo inoltre l'equilibrio ionico alterato con emettitori elettronici di anioni (ioni negativi). E' da sottolineare che l'installazione di emettitori di anioni da soli, senza eliminare il particolato, ha un effetto deleterio: le particelle in sospensione vengono prima neutralizzate, poi caricate negativamente provocandone comunque la precipitazione sulle superfici degli ambienti. E' dunque assolutamente necessario eliminare i grossi ioni inquinanti costituiti dal particolato e dall'aerosol in sospensione, in modo da permettere la vita e la diffusione dei piccoli ioni utili a ricreare il corretto equilibrio elettrico ambientale. Nell'abiente esterno, come visto precedentemente, una situazione ideale è rappresentata da una concentrazione di circa 2000 piccoli ioni per centimetro cubo d'aria, con una leggera prevalenza di ioni negativi:per ricreare la stessa situazione negli ambienti chiusi, generalmente è indicata l'immissione di quantità calibrate di ioni negativi, per contrastare l'eccesso di ioni positivi provocato dallo sfregamento dell'aria sulle superfici (vetro, plastica) e dall'utilizzo in ambiente di macchine ad alta tensione positiva (televisori, monitor per computers, videoterminali,fotocopiatrici e stampanti laser). Come nel caso dell'aria emessa dalle bocchette, anche per l'atmosfera ambientale è indispensabile eliminare gli inquinanti che possono formare grossi ioni e precipitare sulle superfici,oppure essere respirati dagli occupanti. Con un progetto accurato, ovesia possibile, ciò può essere fatto per mezzo dell'impiantodi condizionamento canalizzato, dotato di filtri appropriati sull'aria primaria e di ripresa, nonchè di dispositivi generatori di anioni(ioni negativi), in prossimità delle bocchette di immissione. Dovenon si possa ricorrere all'impianto canalizzato, sarà indicato l'impiegodi appositi purificatori, in grado di aspirare l'aria carica di inquinanti reimmettendola quindi nell'ambiente pura e bilanciata ionicamente, peril massimo confort degli occupanti.
Figura 1
Meccanismo di formazione dei grandi e piccoli ioni secondoLangevin: le radiazioni ionizzanti agiscono sulle molecole dei gas atmosferici,provocando la formazione di una molecola ionizzata positivamente e di unelettrone. Quest'ultimo viene acquisito da una molecola neutra formando una molecola ionizzata negativamente. Le molecole ionizzate formano i piccoli ioni, i quali, aggregandosi a grosse particelle neutre in sospensione nell'aria(aerosol, particolato), formano i grossi ioni, detti di Langevin. I piccoli e i grossi ioni negativi e positivi possono, ricombinandosi, originare piccole e grandi particelle neutre.
Ambiente ioni positivi per cm3 ioni negativi per cm3 rapporto ioni + / -
Ambiente terapeutico 1000 9000 0,1:1
Aria di montagna 2500 2000 1,25:1
Ambiente rurale 1800 1500 1,2:1
Ambiente urbano 600 500 1,2:1
Atmosfera pre-temporalesca 3000 800 3,75:1
Atmosfera post-temporalesca 800 2500 0,32:1
Industria leggera 400 250 1,6:1
Ufficio / appartamento 200 150 1,33:1
Piccoli locali 80 20 4:1
Veicoli mobili chiusi 80 20 4:1
Situazione ottimale 800 1000 0,8:1
Tabella 1,
Tipiche concentrazioni ioniche in ambienti e situazioni diverse: come si vede, gli ambienti chiusi sono generalmente poveri di ioni, con una netta prevalenza di ioni positivi. Significativo il fatto che il rapporto ioni positivi / negativi in alcuni locali sia molto simile a quello della atmosfera pre-temporalesca, associata notoriamente a sensazioni di ansia e di disagio.
Figura 2
Lungo le canalizzazioni l'aria viene caricata positivamente per attrito;in questo modo vengono elettrizzate le particelle in sospensione che si depositano in prossimità delle bocchette: inoltre vengono diffusi ioni positivi in eccesso nell' ambiente. Per ovviare a questi inconvenienti,le condotte devono essere messe a terra, l'aria deve essere filtrata efficacemente ed arricchita di ioni negativi prima dell'immissione nel locale.
Figura 3
In assenza di impianto canalizzato, per ripristinare un corretto equilibrio ionico è necessario utilizzare un purificatore-ionizzatore in grado di aspirare l'aria inquinata e reimmetterla nell'ambiente pulita ed arricchita di anioni. Gli apparecchi più moderni attivano automaticamente laionizzazione solo dopo la completa rimozione del particolato.
Bibliografia
G.W.K. King, Air ionization and itseffects on well being and stress and its biological effectcs, AIBC Bulletin,vol. 2, n° 2, American Institute of Biomedical Climatology, June 1989
G.R. Rager (a cura di), AA.VV., Problèmesd'ionisation et d'aero-ionisation, Maloine S.A. èditeur, Paris,1975
I Benefici degli ioni negativi
Tutto sugli ioni
Gli ioni sono delle particelle cariche nell'aria che si formano quando una dose sufficiente di energia agisce su una molecola, come il diossido di carbonio, l'ossigeno, l'acqua o l'azoto per emettere un elettrone dalla molecola rilasciando uno ione caricato positivamente. L'elettrone spostato si attacca ad una molecola vicina, che diventa quindi uno ione caricato negativamente. E' lo ione negativo dell'ossigeno quello che più ci influenza. Avete presente la sensazione che si prova vicino ad una cascata o in alta montagna? Questi sono due posti dove si trovano migliaia di ioni negativi. Essi hanno effetto sulla biochimica umana.
Normalmente il numero degli ioni nell'aria fresca di campagna è da 2000 a 4000 ioni negativi per centimetro cubo (circa le dimensioni di una zolletta di zucchero). Alle cascate Yosemite, sperimentereste più di 100,000 ioni negativi per centimetro cubo. D'altra parte, il livello è molto al di sotto di 100 per centimetro cubo sulle autostrade di Los Angeles nelle ore di punta.
Mentre la ionizzazione dell'aria è obbligatoria in molti ospedali e luoghi di lavoro europei e russi, nel nostro Paese è venuta alla luce solo recentemente, con la crescita del problema dell'aria tossica negli ambienti urbani.
"Ioni e consapevolezza" Whole Self, Primavera 1991
Cause della carenza di ioni negativi
La ricerca ha dimostrato che le aree inquinate sia al chiuso che all'aria aperta hanno dei livelli molto bassi di ioni negativi, e livelli molto alti di ioni positivi. Sembrerebbe che tutti o quasi gli ioni negativi disponibili si fossero esauriti nella loro lotta con gli agenti contaminanti. Anche i venti caldi e secchi come il Santa Ana o i venti Witches (letteralmente “venti delle streghe” n.d.t.) privano l'aria degli ioni negativi.
Effetti dell'esposizione agli ioni negativi
Degli studi hanno dimostrato che alcune persone diventano molto depresse quando il numero degli ioni negativi è molto basso (depressione stagionale).
Un'alta esposizione agli ioni negativi sembrava associata al sentirsi meglio con se, meno sensibili e più ricettivi o tonici (energizzati).
"Aviazione, spazio e medicina ambientale", Agosto 1982.
I risultati indicavano che i soggetti avevano tempi di reazione più veloci ed avevano riferito di sentirsi significativamente più energici in condizioni di ioni atmosferici negativi rispetto a condizioni di aria normali.
"L'influenza degli ioni atmosferici negativi sulla prestazione umana e sull'umore"
L'introduzione di un generatore di ioni negativi ha aumentato i tassi soggettivi di vigilanza, la freschezza atmosferica e il calore ambientale e personale. Gli ioni hanno ridotto l'ansia, la tensione e li hanno aiutati a respirare più facilmente.
"L'effetto ione"
Dr. Bob Arnot
"Se i burrascosi venti invernali che soffiano attraverso la nazione questa settimana ti stanno buttando giù, c'è una buona ragione. I ricercatori ora credono che i venti “cattivi” caccino via delle particelle subatomiche altamente cariche che si chiamano ioni negativi dall'aria intorno a noi, contribuendo ad una forma stagionale di depressione. Ecco perché. I livelli di una sostanza chimica cerebrale responsabile dell'umore che si chiama serotonina, sono spesso più bassi nei casi di depressione stagionale. I livelli di serotonina possono essere aumentati attraverso una maggiore esposizione alla luce o con antidepressivi come il Prozac. I ricercatori dicono anche che gli ioni negativi possono aumentare i livelli cerebrali di serotonina.
Uno studio riportato nel numero corrente della “Rivista di medicina alternativa e complementare” ha concluso che il 58 percento dei pazienti trattati con ioni negativi ad alta densità hanno avuto un significativo sollievo nei loro sintomi, quasi identico al numero di miglioramenti riscontrati con i farmaci, ma senza gli effetti collaterali degli stessi.
Trascrizione del notiziario della CBS del 14/2/95 6:30-7:00 PM, con Connie Chung.
L'introduzione di un generatore di ioni negativi ha aumentato il tasso soggettivo di vigilanza, la freschezza atmosferica ed il calore ambientale e personale. Gli ioni hanno ridotto il tasso di lamentele di mal di testa del 50% e ridotto significativamente il numero di disturbi di nausea e vertigini.
L'influenza degli ioni atmosferici, della temperatura e dell'umidità sul benessere e sull’agio soggettivi.” Rivista di psicologia ambientale, Dicembre 1981.
Sono stati studiati gli effetti della ionizzazione positiva o negativa artificiale dell'aria sullo svolgimento di compiti psicomotori su 25 uomini in buona salute dai 18 ai 26 anni. Sono stati usati 3 ambienti di prova : naturale, con ionizzazione negativa e con ionizzazione positiva. Alla ionizzazione negativa si è associato un significativo incremento delle prestazioni rispetto ai controlli.”
"Gli ioni atmosferici e la prestazione umana" Ergonomics, aprile 1978.
10 Radioattività ambientale e dose annua assorbita
Anteprima della sezione
Nell’ambiente esiste un fondo di radioattività naturale generato dai raggi cosmici e dagli elementi radioattivi naturali presenti nelle rocce e nella biosfera. Il contributo più importante, pari a circa il 52%, a questo fondo di radioattività dell’ambiente si deve all’uranio 238 e ai suoi discendenti della serie radioattiva di cui è capostipite, in particolare il radon. Il 16,6% circa è ascrivibile invece al torio 232 e ai suoi discendenti; il 15% a isotopi quali il potassio 40 e il rubidio 87, e un altro 15% ai raggi cosmici, che, benché schermati dagli strati alti dell’atmosfera, penetrano in minima percentuale fino alla biosfera. Il totale corrisponde a una dose di circa 130 mRem all’anno.
Se si vuole calcolare la dose a cui un essere umano è normalmente soggetto, tuttavia, si deve aggiungere una componente dovuta alle eventuali esposizioni a radiazioni artificiali: quelle provenienti da radioterapie e analisi radiologiche (circa 46 mRem all’anno), quelle immesse nell’ambiente dai test nucleari (circa 2 mRem all’anno), quelle riconducibili all’attività delle centrali nucleari (circa 0,2 mRem all’anno). Questi contributi portano la dose annua assorbita a circa 200 mRem all’anno. Per avere un’idea degli effetti che queste dosi possono sortire sull’organismo, si consideri che una quantità di radiazioni compresa tra 0 e 25 Rem (1 Rem = 1000 mRem) non produce in genere alcun effetto osservabile; tra 25 e 100 Rem si osservano piccole variazioni nella composizione del sangue; tra 100 e 200 Rem si avverte nausea e affaticamento, oltre a sostanziali variazioni della composizione del sangue e, in pochissimi casi, la morte; si ha invece alta possibilità di morte per dosi superiori ai 200 Rem.
PREMESSA
Cap.1
Da tempo nei Paesi più attenti e sensibili alla problematica della " salubrità ambientale" negli spazi abitati, sono stati presi in considerazione tutti quei parametri legati ai fenomeni elettrici e magnetici che oggi ( alla luce dei progressi compiuti in campo medico e scientifico ) come ben sappiamo rivestono molta importatanza per la nostra salute.
E' infatti da ritenersi incompleta quell'analisi della qualità dell' aria , o comunque della vita all'interno delle abitazioni , che non tenga conto di tutti i parametri che intervengono in modo più o meno rilevante nelle modificazioni del sistema stesso.
Purtroppo ancora oggi vi sono Paesi , tra i quali I'Italia , in cui le conoscenze scientifiche riguardanti queste problematiche non vanno oltre il livello di ricerca; al contrario in altri Paesi ( U.S.A. , Norvegia , Svezia , Danimarca ecc) vengono seriamente tenute in considerazione dagli Enti e dagli Istituti preposti ai controlli ed allo studio delle condizioni di vita della popolazione, e quindi tradotte in una serie di misure di prevenzione atte a diminuire i rischi per la salute
BIOLOGIA ARCHITETTONICA.
Cap. 2
Troppo spesso si studiano e si analizzano le varie componenti dei sistemi e delle strutture abitative, senza tenere conto che vi sono altri " agenti inquinanti " oltre agli ossidi di azoto , alla formaldeide , al pentaclorofenolo ecc . , o dimenticando che i parametri fisici ed ambientali che definiscono il grado del comfort abitativo non sono solo temperatura , umidità , e movimento d' aria.
E' infatti emerso, da numerosi studi e ricerche condotte negli U.S.A. e nei Paesi del Nord Europa ,che esiste un rapporto diretto tra alcune malattie e disturbi accusati da persone che passano la maggior parte del loro tempo in luoghi chiusi ( uffici , fabbriche , magazzini ... ) , e la presenza di forti squilibri elettrici ( campi elettromagnetici, elettropulsanti ed elettrostatici , radiazioni ionizzanti di basso livello inversioni della carica spaziale con predominanza aero ionica di polarità positiva).
Proprio per questo motivo, nei Paesi in cui le conoscenze in campo di inquinamento ambientale sono più evolute , con il termine BIOLOGIA ARCHITETTONICA si indica quella branca della scienza che studia le azioni e le interazioni biologiche tra 1' uomo e lo " spazio - struttura " abitativa.
Appare infatti evidente la differenza che esiste tra una costruzione tradizionale ed un palazzo di cemento armato in una grossa città ; la naturale presenza di energia elettro-magnetica quanto meno viene alterata dalle strutture artificiali sopracitate che , a volte , possono rivelarsi dei veri e propri bunker elettrici.
Non solo, ma è molto importante tenere in considerazione che individuare il giusto grado di umidità e di temperatura non implica necessariamente I'aver stabilito le condizioni microclimatiche soddisfacenti e confortevoli per gli occupanti; come detto vi sono altri fattori climatici che devono essere considerati.
CARATTERISTICHE FISICHE DELLA IONIZZAZIONE.
Cap. 3
La ionizzazione dell'aria è il fenomeno fisico di scissione di un atomo , o di una molecola , in più parti dotate di carica elettrica la cui somma algebrica è nulla.
Innanzitutto è indispensabile sottolineare che la ionizzazione è un fenomeno naturale che interviene spontaneamente ogni qualvolta una molecola è sottoposta all'azione di un processo energetico in cui la quantità totale di energia ( Et ) e' superiore al valore di Ei ( Energia di ionizzazione ) della molecola stessa.
Quando una radiazione incidente ( con Et > Ei ) entra in collisione con un atomo, lo scambio energetico che si verifica è sufficiente ad estrarre un elettrone dall'orbita più esterna e, a causa dello squilibrio elettrico 1'atomo assume una carica Positiva ( AEROIONE + ) . L'elettrone invece, liberato dal suo legame con il nucleo si fissa immediatamente su un altro atomo che quindi assume una carica Negativa ( AEROIONE - ).
I processi ( o agenti ionizzanti ) che possono indurre la ionizzazione dell'aria sono molteplici:
- Emanazioni radioattive (raggi gamma e raggi X )
- Raggi Cosmici.
- Radiazioni U.V.
ed inoltre :
- Collisioni ed Urti tra corpuscoli dotati di energia cinetica ( ionizzazione d'urto ).
- Emissioni di fotoelettroni, termoelettroni, fiamme scariche elettriche, frizione molecolare ...
- Fattori e parametri elettro meteorologici e climatologici.
Dipendentemente dalla saturazione della corona periferica ogni atomo ha una probabilità ben definita di assumere una carica elettrica positiva o negativa.
Gli ioni atmosferici (o aeroioni) si possono classificare in trè categorie :
- PICCOLI
Sono composti da piccoli "grappoli" di molecole (diametro 0.001 - 0.003 micron ) con grande mobilità ed una carica elettrica elementare di 1.6*10 E-9 Coulomb. Hanno una vita media molto breve soprattutto in presenza di umidità.
- INTERMEDI
Sono costituiti da grossi agglomerati molecolari con diametro di 0.003 - 0.03 micron. La loro presenza è alquanto rara poichè anche per livelli molto bassi di umidita' si trasformano in grossi ioni.
- GRANDI
Sono chiamati anche ioni di LANGEVIN, hanno una mobilità relativamente bassa e, come gli ioni intermedi non hanno praticamente effetto sulla conducibilità' elettrica dell' aria.
Molto spesso su di essi condensa il vapore acqueo formando i cosiddetti nuclei di condensazione.
L'IMPORTANZA DELLA IONIZZAZIONE DELL' ARIA.
Cap. 4
L'analisi bioclimatologica delle attività' umane considera come strutture ambientali sia quelle Interne che quelle esterne ( endosferiche ) ; Infatti deve sempre essere tenuto in considerazione che il microclima confinato è ugualmente soggetto alla Influenza ( positiva o negativa ) dell'ambiente spaziale esterno : temperatura , umidità , pressione, Ionizzazione, raggi cosmici.
Premesso questo , risulta facile sottolineare come lo studio del sistema , inteso come microclima circoscritto in cui l'uomo vive, comprende un numero di variabili tale che risulta molto complesso individuare con precisione gli effetti e le interazioni di ogni singolo parametro.
Non dobbiamo infatti dimenticare che le interazioni tra i composti inquinanti e i pararnetri climatologici hanno effetti sinergici.
Il grado di ionizzazione dell'aria dipende da fattori meteorologici , climatologici ed ambientali ; in condizioni naturali esiste un rapporto di circa 1 : 1.2 tra le cariche elettriche negative e quelle positive.
La concentrazione degli ioni gassosi presenti nell' aria tende a diminuire in presenza di inquinamento ; in particolar modo per quanto riguarda 1' inquinamento dell' aria all'interno degli spazi abitati e' indispensabile mettere in evidenza come i condizionatori d' aria, gli impianti di riscaldamento, il fumo di sigarette, terminali video ed altre apparecchiature elettriche usate in casa o negli ambienti di lavoro riducano drasticamente la concentrazione degli aeroioni negativi.
Oggi vi sono moltissime ricerche condotte con stretto rigore scientifico e supportate da Istituti ed Enti nazionali ed internazionali che dimostrano con estrema evidenza come la carica elettrica dell' aria , riferita alla presenza di piccoli aeroioni eserciti un' influenza tutt'altro che trascurabile.
Naturalmente il presupposto d' analisi deve essere puramente scientifico e non lucroso ; ogni giorno siamo infatti bombardati da false informazioni pubblicate su giornali e riviste da produttori poco seri che attribuiscono agli ioni negativi effetti miracolosi, e' necessario sempre valutare attentamente e prendere in considerazione solo le informazioni corredate di dimostrazione scientifica.
Il Prof. Kruger ( Biomedicai Laboratory Science Division and Naval Biological Laboratory , University of California U.S.A.' ha dimostrato che gli aeroioni negativi provocano una diminuzione del tasso di 5-HT ( serotonina ) , ed incrementano l'attività' ciliare sulla mucosa tracheale ; Gli aeroioni positivi invece agiscono in senso opposto.
Gli effetti benefici che gli aeroioni negativi esercitano sull'uomo sono molteplici , tuttavia dato il contesto della nostra valutazione analizzeremo il problema da un punto di vista strettamente tecnico.
Il prof. Alfredo MURRI ( fondatore dell'Osservatorio Geofisico Sperimentale di Macerata ) ha dimostrato in lunghi anni di ricerche in campo elettro-meteorologico e ciimatologico che alla predominanza della carica positiva dell'aria e' sempre associabile la presenza di un agente inquinante :
dalle sue ricerche infatti emerge chiaramente che umidità, polvere , gas di combustione, abbassano la conducibilità' elettrica dell'aria ed associano ad essa una carica positiva che tende a ridurre sensibilmente il contributo delle cariche negative.
Questo problema assume notevole importanza soprattutto nello studio della qualità dell' aria all'interno delle abitazioni dove la presenza della polvere , di gas provenienti da combustioni ,di apparecchiature elettriche , di impianti di condizionamento e di riscaldamento, e la presenza di persone crea degli squilibri senz' altro non trascurabili .
Per quanto riguarda gli impianti di condizionamento dell'aria il problema che si pone assume dimensioni notevoli.
Infatti oltre agli effetti negativi che tutti conoscono devono essere tenuti in considerazione anche altri aspetti legati alle strutture stesse degli impianti :
1'aria che fluisce all'interno delle condotte di aspirazione ( metalliche ) viene privata delle cariche negative che dotate di maggiore mobilità si scaricano verso terra più facilmente che non le cariche positive.
Quindi 1' aria di un ambiente in cui è installato un condizionatore risulta impoverita della sua naturale carica elettrica e presenterà un eccesso di aeroioni positivi.
Da alcune ricerche condotte in edifici con impianti a ricircolazione d ' aria , è emerso inoltre che in questi casi l'ambiente e' praticamente deionizzato.
Se teniamo conto infine degli altri fattori (sopracitati) che all'interno delle abitazioni intervengono nella distruzione dei piccoli aeroioni ci rendiamo subito conto che il problema non può' essere trascurato, soprattutto nel momento in cui si effettua un' analisi delle condizioni microclimatiche ambientali.
DIAGNOSI E SUCCESSIVO INTERVENTO DI BONIFICA
Cap. 5
Le procedure tecniche che devono essere seguite in un' analisi della salubrità ambientale di un microclima circoscritto prevedono la misura di tutti i parametri che , come già detto , condizionano l'ambiente stesso .
Nel contesto della nostra valutazione prendiamo in esame le correlazioni tra la concentrazione degli aeroioni e 1'inquinamento dell'aria da microorganismi, composti organici volatili ( VOC ), particolato, pollini , ecc .
Innanzitutto e' necessario specificare che installare un purificatore d'aria dotato di dispositivi ionizzatori, non implica necessariamente aver risolto tutti i problemi di inquinamento e di comfort abitativo.
Tuttavia i risultati che si ottengono sono senz'altro apprezzabili e comunque , anche se non sollevano dalla necessità di eliminare tutte le cause di insalubrità' ambientale costituiscono in ogni caso un valido presupposto di risanamento.
La soluzione più' idonea , che quindi porterebbe i maggiori benefici, è l' impianto di ionizzazione e depurazione integrato nelle strutture dell' edifcio ; purtroppo le conoscenze degli addetti ai lavori nei riguardi di questo tipo di depurazione dell'aria sono ancora lontane per consentire questo tipo di progettazione.
Parleremo quindi di apparecchi da installare come ausilio di bonifica in case , uffici , ospedali ecc.
STRUMENTI E METODI
Cap. 6
Per la misura della Ionizzazione dell' aria si Impiega un misuratore di carica spaziale, in cui la mobilita' limite degli aeroioni che si Intende misurare sia corrispondente a quella del piccoli aeroioni ( K= 0.85 Cm 2 / V*Sec ).
Nel nostro caso abbiamo utilizzato lo ION-METER PN 2001 di fabbricazione PERISO ; uno strumento in grado di rilevare anche la singola carica elettronica con un campo di misura da O a 400 milioni di Ioni / Cm3 e con una risoluzione di 1000 ioni su 2.5 milioni.
Gestito da un microprocessore , svolge autonomamente tutte le funzioni di azzeramento , start , stop , adeguamento scale e se collegato con un PC esterno consente l'elaborazione immediata del dati raccolti.
Date le dimensioni ridotte si presta facilmente per misure in ambienti interni , dove può anche essere posizionato su un carrello rack che raccoglie altri strumenti atti a rilevazioni di parametri ambientali.
Per la misura dei microorganismi si utilizza un apposito campionatore d'aria a volumi programmabili , all'interno del quale vengono di volta in volta inserite delle piastre di Petri con i terreni di coltura sui cui avverrà lo sviluppo.
Per gli altri parametri invece si utilizzano gli strumenti che facilmente si trovano in commercio ( contatore di particelle, di nuclei di condensazione , di gas , ecc.) .
I dispositivi di depurazione dell'aria invece vengono scelti in relazione alla volumetria del locale da risanare e al tipo di attività' che accoglie ; essenzialmente si suole dividere le due categorie : civile ed industriale.
La costruzione degli apparecchi avviene con materiali sintetici ecologici , e cosi' pure per il filtro , che anche se incenerito non produce sostanza tossiche.
TECNICA DELLA DEPURAZIONE
Cap. 7
In linea generale si può sintetizzare il principio di funzionamento come segue :
gli apparecchi sono dotati di un silenzioso ventilatore tramite il quale avviene il riciclo forzato dell 'aria ; le particelle inquinanti presenti nell'aria ambiente caricata elettricamente dagli appositi dispositivi, vengono quindi catturate grazie alla doppia azione di forze coulombiane e d' induzione elettronica dalle fibre elettrizzate del filtro.
Il filtro , frutto di lunghe ricerche svolte alla 3M e' costituito da un prefiltro meccanico e dal filtro vero e proprio , composto da una moltitudine di fibre sintetiche elettrizzate e stabilizzate , in grado di trattenere il 95 % delle particelle aventi diametro 0.1 micron .
L'efficacia della depurazione di questi apparecchi e' insita nel concetto stesso di funzionamento ; infatti è grazie al fenomeno di ionizzazione degli agenti inquinanti che e' possibile eliminarli nella quasi totalità.
E ciò non solo nel caso di particolato e polvere ma anche , e soprattutto , nel caso di sostanze gassose, VOC.
Infatti sono state eseguite numerose ricerche , soprattutto in Germania , nei paesi del Nord Europa e in America con le quali si e' dimostrato l'efficacia della ionizzazione nell' abbattimento di sostanze gassose nocive alla salute (per esempio la Formaldeide, il 3,4 Benzopirene, gli Idrocarburi incombusti, il fumo di sigarette, gli ossidi di zolfo, di Carbonio, ecc.).
Per quanto riguarda invece la depurazione da microorganismi è di fondamentale importanza evidenziare l'assoluta efficacia degli aeroioni negativi : possiamo citare a questo proposito una ricerca ( ma ve ne sono molte altre condotte in molti altri paesi ) eseguita presso la Cllnica Mangiagalli di Milano :
In un locale di 200 m3 adibito a sala visite sono stati installati 4 dispositivi ionizzatori mod. ISO-ION NR 2. che garantivano un ricambio d'aria circa ogni ora.
Sono stati quindi rilevati i livelli di contaminazione batterica in due punti differenti utilizzando delle piastre di Petri a carica totale prima e dopo aver installato e messo in funzione i purificatori :
i risultati sono stati eccellenti , evidenziando la notevole capacita' di depurazione della ionizzazione negativa.
Infatti si può ' vedere molto chiaramente dal grafico riportato come , con il trascorrere del tempo , la concentrazione dei batteri diminuisce.
Dopo 24 ore di ionizzazione , si è verificata una diminuzione della carica batterica del 41% nel punto A e del 69% nel punto B.
Dopo una successiva ora di ionizzazione si e' verificata una ulteriore diminuzione della carica batterica del 62% nel punto A e del 42 % nel punto B
CONCLUSIONI
Cap. 8
A questo punto ci si rende conto con estrema chiarezza della importanza che riveste la ionizzazione negativa dell 'aria.
Correttamente impiegata, con apparecchiature idonee , sicure e garantite dal marchio di qualità e con un' attenta analisi della situazione climatologica, operata tramile appositi strumenti in grado di rilevare il livello della carica spaziale , è possibile ottenere risultati che, considerato il rapporto necessita'- costi -risultati non sono raggiungibili con altri sistemi o apparecchiature oggi in commercio.
E considerando 1'entità del problema costituito dall' inquinamento dell'aria negli ambienti interni , non si può fare a meno di notare come sia estremamente vantaggioso ed economico questo sistema di depurazione , che tra l'altro consente di eliminare alcuni inquinanti (per esempio la formaldeide ) contro i quali i sistemi oggi a disposizione sono , a volte , economicamente inaccettabili o , nella maggior parte dei casi , inattuabili.
E' comunque necessario stare in guardia dai produttori poco onesti che commercializzano apparecchiature prive di marchi di qualità e non sottoposte a severi controlli circa l'emissione di sostanze nocive : il dispositivo che da' origine al fenomeno fisico della ionizzazione dell'aria deve essere rigorosamente progettato seguendo e criiteri di assoluta sicurezza.
Infatti e' doveroso far notare che riprodurre artificialmente il fenomeno della ionizzazione dell'aria non e' cosi' semplice come si potrebbe pensare : si corre infatti il rischio di generare ozono oppure di ossidare l'azoto o altri gas presenti nell'aria peggiorando così la situazione tra l'altro già precaria.
In definitiva quindi possiamo concludere questa breve analisi considerando che quando si studiano i problemi degli ambienti di vita in relazione alla salute dei cittadini e' necessario prendere in considerazione tutti i parametri che intervengono , tra i quali quindi anche la ionizzazione dell' aria , fino ad oggi trascurata.
BIBLIOGRAFIA
ALBRECHTSEN ( 1979 ) : Thè effect of electric fleids in mental work.
CENSI - FUSARI - MURRI - SCUTERINI : Correlazioni fra parametri elettrici atmosferici ed alcuni fenomeni biologici.
A. MURRI " C. SCUTERINI : Ricerche sulla carica spaziale.
FRIGERIO - CALDARELLA - MOLTENI - GARLASCHI - ROSSI : Ionizzazione artificiale dell' aria e riduzione della carica batterica in una sala operatoria ginecologica.
HAWKINS - BARKER ( 1978 ) : Air lons and Human Performance.
HAWKINSON - BARBER ( 1981 ) : Thè industriai Hyglene significane e of small air lons.
JONASSEN ( 1985 ) : Thè physics of air ionisation.
KRUEGER " KOTAKA : Thè effect of air lons on experimental respiratory infections.
KRUEGER - BROOK » REED ( 1975 ) : Air lon Action on Bacterla. KRUEGER ( 1985 ) : Thè blological effect of air lons. LOMBARDO : L' elettroaerosolterapla dell' asma bronchiale*
MOESE - FISCHER : (1976 ) Research of Blological Effects of Electric Enviromental Factors.
SULMAN ( 1976 ) : Health . weather and climate.
SULMAN " LEVY - LUNKAN - PFEIFER " TAL. : Absence of Harmfui Effects of Protracted Negative Air Ionisation.
SVAB ( 1976 ) : lonizzatori per uso medico.
dizionario
ionizzazione
Con il termine ionizzazione si intende quel processo atto ad immettere nell'aria una certa quantità di ioni negativi, in modo da ristabilire i livelli di equilibrio che normalmente si trovano in natura.
Gli ioni negativi sono molto importanti e rappresentano un'incredibile risorsa per l'uomo: essi favoriscono la concentrazione, danno vitalità e benessere all'organismo.
Tra gli effetti benefici della ionizzazione dell′aria abbiamo:
• La normalizzazione della pressione arteriosa;
• La diminuzione della velocità di ossidazione dei globuli rossi;
• Il miglioramento dei processi respiratori dei tessuti;
• La normalizzazione dello scambio di vitamine (B1, B6, PP, C);
• L′aumento del livello di ossigeno nel sangue;
• L′aumento della capacità di termoregolazione;
• La normalizzazione del sistema cardiovascolare e motorio;
Il rapporto ottimale tra gli ioni dovrebbe essere di 3 ioni negativi per ogni ione positivo.
Purtroppo questo equilibrio viene spesso stravolto dall'attività umana che, con l'emissione di gas serra, polveri inquinanti, fumi e smili, può portare a volte il rapporto ad 1 contro 600, con conseguenze facilmente immaginabili sulla salute dell'individuo, causando, tra l'altro, spossatezza, asma, allergie e scarsa concentrazione.
Lo strumento che effettua l'azione di ionizzazione viene chiamato Ionizzatore
copyright © 2008 M.P. International S.r.l. - Gruppo Airone Italia
Con l'utilizzo di materiale ionizzante naturale trattato a livello nanotecnologico, disperso nei rivestimenti verniciati e plastiche, si possono ottenere buoni livelli di ionizzazione negativa, che vanno a compensare la presenza di ioni positivi(dannosi per la salute), portando il rapporto tra ioni molto favorevole alla condizione negativa, l'ipotesi migliore per classificare un ambiente in cui vivere.
The Positive Health Benefits of Negative Ions
Air pollution is a serious, though often unrecognized health problem. Epidemiological studies consistently point to a direct link between urban air pollution – especially particulate pollution created by combustion powered vehicles and power generation plants – and cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases. (1) Long-term exposure to particulate pollution – tiny particles smaller than 10 microns (a human hair is 70 microns wide) – is known to increase illness and death rates from lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and emphysema. Additionally, exposure to other airborne pollutants, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and ozone (O3), is associated with development of asthma, bronchitis, and respiratory infections. (2)European researchers investigated the risks of long-term exposure to traffic pollution in a study examining 5000 volunteers selected from the ongoing Netherlands Cohort study on Diet and Cancer (NLCS). They discovered that people living near major roads (and therefore exposed to higher levels of traffic-related air pollution) were more likely to die from cardiopulmonary disease or lung cancer than their rural peers, leading the authors to conclude that 'long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution may shorten life expectancy. (3)
Air Pollution Linked to Heart Damage
In addition to causing lung damage, air pollution is now also
recognized as a threat to cardiovascular health. Reporting in the March
6, 2002 Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA),
researchers examined long-term health data on 500,000 individuals to
compare increases in air pollution levels with incidence of death. They
discovered that when air pollution levels suddenly increased, in
addition to expected increases in deaths from asthma, pneumonia, and
emphysema, there was an unexpected increase in the number of deaths
related to heart attacks and stroke. Most surprising was the finding
that when air pollution levels rose, so did deaths from all causes, not
just those related to the heart and lungs (Fig. 1). (4) 
This was shown to be the case when scientists working in the Netherlands exposed rats to high levels of particulate air pollution. Following exposure, the researchers found that plasma levels of fibrinogen were elevated by 20 percent, which could presumably increase blood viscosity, leading to decreased tissue blood flow. They also measured a 400 percent jump in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and a 350 percent increase in nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in lung fluids. The researchers speculated that as particulates lodge in lung tissues they induce an increase in the production of nitric oxide (NO). Under normal conditions nitric oxide is an important neurotransmitter that aids numerous signaling pathways involved in motor learning, protein modification, arterial dilation and immune defense. But when conditions trigger the overproduction of NO as seen in the Netherlands study, the result is serious damage to the endothelial cells lining the blood vessels of the lungs. (5)
When Japanese researchers exposed guinea pigs to particulates from diesel exhaust, the lungs showed a significant elevation of leukotrienes and eosinophils, two important biomarkers of inflammation and cytotoxicity commonly observed in cases of chronic obstructive lung disease (COLD). The researchers noted that these findings indicate that chronic exposure to diesel exhaust induces continuous inflammation and overproduction of mucus and phospholipids in the lung. (6)
Another mechanism implicated in air pollution-related heart failures involves bone marrow and atherosclerotic plaques. Researchers in Vancouver, British Columbia found that exposure to high levels of air pollution stimulates bone marrow to release leukocytes and platelets that accumulate preferentially in pulmonary capillaries. In addition to causing damage to lung tissues, the researchers also observed that inhalation of particulate pollution causes changes in atherosclerotic plaque lesions that make the deposits more vulnerable to rupture.
They postulated that exposure to particulate air pollution induces a systemic inflammatory response that includes the release of inflammatory mediators that stimulate bone marrow to release leukocytes and platelets, leading to lung inflammation and changes of atherosclerotic plaque, making them more vulnerable to rupture. (7)
Diabetics and Elderly at Increased Risk
Diabetics are particularly susceptible to cardiovascular damage
caused by airborne pollution. A recent study published in the journal
Epidemiology examined Medicare records and hospital admissions in US
cities: Chicago, Detroit, Pittsburgh, and Seattle. Looking at records
from 1988 to 1994 they found that diabetics were twice as likely as
non-diabetics to be admitted to a hospital with a cardiovascular problem
caused by airborne particulate pollution. They also found that persons
75 years of age and older also faced a higher risk of cardiovascular
injury. (8)
Children and Air Pollution
Children are particularly at risk for health issues related to air
pollution. Chronic exposure to particulates, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen
dioxide have been associated with up to 300 percent increases in
nonspecific chronic respiratory symptoms. Exposure to automotive
pollution, particularly from truck and diesel exhaust, has been shown to
cause significant increases in respiratory symptoms and decreased lung
function. (9)To examine the relationship between traffic-related air pollution and childhood development of asthma and other childhood respiratory diseases and infections, researchers in the Netherlands looked at data from some 4,000 babies born in the Netherlands. The health of the children was linked to measurements of traffic-generated air pollution (nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter less than 2.5 microns in diameter, and soot) in the homes of each subject. Their study found that, by the age of two years, children exposed to higher levels of air pollutants were more likely to suffer from wheezing, physician-diagnosed asthma, ear/nose/throat infections, and flu/serious colds. (10)
Part of the problem for children is that studies show that – relative to their size – children inhale more deeply and trap more airborne particles and pollutants in their lungs than either adolescents or adults. (11) Children also have higher metabolic rates than adults, breathe more than adults, and spend more time outdoors than adults, exacerbating their susceptibility to pollution-related health problems.
Children's Growth Stunted
When Polish researchers examined the effects of air pollution in
Krakow they discovered that children living in those areas with the
highest levels of air pollution suffered from stunted growth. After
collecting data on 958 children and assessing body growth rates by
height changes they found that body growth rates for children from the
most highly polluted area was lower by 1.5 cm over a 2-year period than
those from the control area. The compromising effect of air pollution on
height gains was about the same for both short and tall children. (12)
Air Pollution and DNA Mutations
New research shows that the health threat posed by air pollution
may actually affect children even before they are born. On December 9,
2002, Canadian researchers published a study revealing that animals
exposed to polluted air close to a steel mill suffered genetic damage
and produced fewer offspring. Most alarming was the discovery that
damaged DNA was being passed on to offspring by their fathers. While
virtually all mutations were inherited from the father mice, the
researchers said this doesn't mean that females are not susceptible.
What it does suggest is that steel workers, who are mostly male, may be
at extra risk of similar damage.Christopher Somers, James Quinn, and colleagues published an earlier study that found that gulls living near a steel mill on Lake Ontario suffered from genetic mutations. In a current study the researchers raised two groups of mice – the first a half-mile downwind of a steel mill on Lake Ontario, and the second about 20 miles away. The mice breathing the polluted air had twice as many mutations in their DNA as the mice breathing fresh country air. (13)
The findings suggest that steel mill workers and people living near those mills should be checked for damage to their health, said the researchers, at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario. "Our findings suggest that there is an urgent need to investigate the genetic consequences associated with exposure to chemical pollution through the inhalation of urban and industrial air."
Ironically, the study was originally aimed at showing how efforts to clean up pollution around the steel mill had improved the environment. 'This had been one of the most polluted places, if not the most polluted place in Canada,' stated Christopher Somers, one of the lead researchers. 'There has been a concerted effort to clean up Hamilton harbor and reduce air emissions.' The experiment had been aimed at showing these had helped. ''We haven't really seen that,'' he said.
Protecting Your Lungs
While government, business and environmental interests wrangle over
a morass of economic, legislative and technological solutions for
cleaning up polluted air, the vital issue facing individuals is how best
to protect their health. Currently over 75 million people in the US
live in counties where the air concentrations of particulate matter
smaller than 2.5 microns (PM2.5) exceed safe levels (Fig. 2.). (14) 
While living away from polluted urban centers is an
obvious choice, this option is not always possible. Nor is it always
effective. Air currents and weather patterns can move polluted air out
of urban manufacturing centers and into rural areas where pollution can
concentrate to a dangerous degree. Additionally, modern farming produces
more food with fewer workers, using improved productivity methods that
increasingly rely on the use of agricultural pesticides and chemicals,
and irrigation pumps and tractors powered by diesel engines. (15)
Staying indoors does not guarantee better air quality, either.
Several recent studies have indicated that much of the significant
health risk associated with exposure to fine particles actually occurred
indoors. (16) And many individuals at increased risk of health
complications following exposure to high particle concentrations, such
as the elderly and those suffering from cardiovascular and pulmonary
diseases, may spend more than 90% of their time indoors, raising new
concerns about the relationship between outdoor particle concentrations
and those found in indoor microenvironments. (17)
Air Purifiers
As the scope of air pollution related health problems grows, so too
does the number of people turning to air purifying solutions for
protection. Home air filtration products offer a number of options,
including electrostatic, UV radiation, water and advanced HEPA
filtration technologies. Until recently, these products – many
engineered for entire houses and buildings – were bulky and expensive to
install and maintain, placing them out of reach for most people.
Recently, a number of consumer products have become available utilizing
ion-generating technology to eliminate airborne pollutants, allergens
and viruses from immediate breathing spaces.These devices work by generating a flow of negative ions that charge and bind together airborne particulate matter, which then clumps and precipitates out of the air. Ion generating devices have been shown to be effective against dust, cigarette smoke, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, viruses, and bacteria. In addition to eliminating harmful particulates from the air, negative ions also have a number of unique health benefits.
Positive Ions - An Ill Wind Blows
Early clues about the biological effect of ions on human health appear as reports of increased irritability, migraine attacks and thromboembolism in response to alterations in atmospheric electrical states that accompany incoming weather fronts. (18)Scientific evidence began to mount in the 1970s when researchers measured metabolic changes in mice and rats in response to changes in ion charge (negative or positive) and concentration, including alterations in serotonin levels and recovery from illness. When exposed to positive ions (which accumulate in the atmosphere at the beginning of a storm) researchers routinely noted that animals became agitated, aggressive and were more prone to respiratory illness. Furthermore, when mice were infected with influenza virus and housed in an environment depleted of all ions, death rates increased, indicating a previously unknown benefit on overall health. (19)
Later, researchers measured the impact of atmospheric electricity on human subjects by monitoring daily changes in urine excretion of neurohormones in samples gathered from 1,000 volunteers exposed to positive ions generated 1 to 2 days prior to the arrival of a storm front. By measuring the changing levels of neurohormones in the 24-hour urinary output of the subjects during normal and weather-stress days, the researchers compiled a profile of changes in levels of serotonin, 5-HIAA (5-hydroxyindole acetic acid, a serotonin metabolite), adrenaline, noradrenaline, histamine and thyroxine.
The researchers found that the electrical charges (positive ionization) engendered by every incoming weather front produce a release of serotonin. (20) They further identified three classes of weather sensitivity reactions:
1. serotonin hyperproduction causing a typical irritation syndrome;Noting that these conditions occur during annual wind storms (Sirocco, Sharav and Santa Ana winds), the authors stated that the effects, "which are mainly due to positive ionization of the air," could be "prevented by negative ionizing apparatuses or specific drug treatment." (21)
2. adrenal deficiency producing a typical exhaustion syndrome;
3. hyperthyroidism with subclinical 'apathetic' thyroid symptoms.
Further evidence of the influence of ions appeared when scientists exposed mice to an atmosphere enriched with either positive or negative ions. While negative ions had no negative effect on the mice, positive ions caused elevations in norepinephrine levels within one day. When exposure to positive ions was continued for longer periods, ranging from 3 to 10 days, norepinephrine levels dropped. The author noted that the results showed that "positive ions cause stress after short time application in excess. After longer exposure, a state of exhaustion can be observed in the form of a lowered norepinephrine level." (22)
Health Benefits of Negative Ions
Just as positive ions build up in the atmosphere prior to a storm
front, negative ions accumulate following a storm. This surfeit of
negative ions has long been associated with improvements in mood and
physical health. Research conducted in the last decade has begun to
support the view that negative ions have a net positive effect on
health.One of the most tantalizing hints regarding negative ions and health surfaced when German researchers discovered a link between catecholamine regulation and lifespan after depriving experimental animals of negative ions. First, researchers at the Goldstein and Lewin Dept. of Medical Research in Stahnsdorf, Germany isolated mice and rats in air-tight, sealed acrylic cases. Next, they filtered the ambient air to remove all negative ions from the sealed cases. Their research led to the discovery that a prolonged deficiency of negative ions led to an accelerated rate of death for the experimental animals. Examination of the animals led researchers to conclude that the results 'strongly suggest that animal death is related to disturbances in neurohormonal regulation and pituitary insufficiency. (23)
Researchers at the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow discovered that negative ions are able to help protect the body from induced physical stress. When the researchers immobilized rats and exposed them to negatively charged air ions they discovered that the ions prevented the development of pathological changes characteristic of acute stress that are observed in untreated rats. The protective action of negative air ions was observed in all the experimental animals independently of their types of behavior. (24)
British researchers at the Centre for Sport and Exercise Sciences in Liverpool exposed male subjects to negative ions and measured physiological responses, including body temperature, heart rate and respiration, while at rest and during exercise. Negative ions were found to significantly improve all physiological states, particularly during rest. Most important was the finding that negative ions are "biologically active and that they do affect the body's circadian rhythmicity." (25)
Another clue to the role of negative ions in health comes from Russian research conducted at the Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Biophysics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, in Pushchino, Russia. Researchers found that exposure to negative ions increased levels of the protective antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) in mammalian erythrocytes. The researchers also discovered minute amounts of H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide), writing, "The primary physiochemical mechanism of beneficial biological action of negative air ions is suggested to be related to the stimulation of superoxide dismutase activity by micromolar concentrations of H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide)." (26)
Summary
While progress has been made in some areas of air pollution, such
as reductions in emissions of lead, sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen
dioxide (NO2) and ozone (O3), air pollution, particularly from
particulates, remains a serious health problem. In addition to damaging
the lungs and heart, air pollution is now recognized as being especially
harmful to children, the elderly, and select sensitive populations,
such as those afflicted with diabetes, cardiopulmonary diseases and
other debilitating illnesses.To address air pollution-related health problems a growing number of people are using personal and home air filtration products that generate negative ions to charge and precipitate airborne particulate matter for removal to create localized zones of improved air quality.
Consumer devices that utilize negative ion-generating technology have been shown to eliminate airborne pollutants, dust, cigarette smoke, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, viruses, and bacteria from the air. Negative ions have long been attributed to improvements in mood and physical health. Research supports the view that negative ions have a net positive effect on health, including improved mood, stabilized catecholamine regulation and circadian rhythm, enhanced recovery from physical exertion and protection from positive ion-related stress and exhaustion disorders.
References
1. Vrang ML, Hertel O, Palmgren F, Wahlin P, Raaschou-Nielsen O,
Loft SH. Effects of traffic-generated ultrafine particles on health.
Ugeskr Laeger 2002 Aug 19;164(34):3937-41.2. Polosa R, Salvi S, Di Maria GU. Allergic susceptibility associated with diesel exhaust particle exposure: clear as mud. Arch Environ Health 2002 May-Jun;57(3):188-93.
3. Hoek G, Brunekreef B, Goldbohm S, Fischer P, van den Brandt PA.Association between mortality and indicators of traffic-related air pollution in the Netherlands: a cohort study. Lancet. 2002 Oct 19;360(9341):1184-5.
4. JAMA March 6, 2002;287:1132-1141.
5. Ulrich MM, Alink GM, Kumarathasan P, Vincent R, Boere AJ, Cassee FR.. Health effects and time course of particulate matter on the cardiopulmonary system in rats with lung inflammation. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2002 Oct 25;65(20):1571-95.
6. Ishihara Y, Kagawa J. Dose-response assessment and effect of particles in guinea pigs exposed chronically to diesel exhaust: analysis of various biological markers in pulmonary alveolar lavage fluid and circulating blood. Inhal Toxicol 2002 Oct;14(10):1049-67.
7. van Eeden SF, Hogg JC. Systemic inflammatory response induced by particulate matter air pollution: the importance of bone-marrow stimulation. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2002 Oct 25;65(20):1597-613.
8. Zanobetti A, Schwartz J. Cardiovascular damage by airborne particles: are diabetics more susceptible? Epidemiology 2002 Sep;13(5):588-92.
9. Nicolai T. Environmental air pollution and lung disease in children. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 1999 Dec;54(6):475-8.
10. Brauer M, Hoek G, Van Vliet P, et al. Air pollution from traffic and the development of respiratory infections and asthmatic and allergic symptoms in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002 Oct 15;166(8):1092-8.
11. Inhalation Toxicology, Sept. 1998;10:831-842.
12. Jedrychowski W, Maugeri U, Jedrychowska-Bianchi I. Body growth rate in preadolescent children and outdoor air quality. Environ Res 2002 Sep;90(1):12-20.
13. Christopher M. Somers, Carole L. Yaukdagger, Paul A. Whitedagger, et. al.. Air pollution induces heritable DNA mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, Vol. 99, Issue 25, 15904-15907, December 10, 2002.
14. EPA, Latest Findings on National Air Quality: 2000 Status and Trends.
15. Smog Check II for All. San Jose Mercury News, Sep. 29, 2002.
16. R.B. Mosley, D.J. Greenwell, L.E. Sparks, Z. Guo, W.G. Tucker, R. Fortmann, C. Whitfield. Penetration of Ambient Fine Particles into the Indoor Environment. Aerosol Science and Technology: Vol. 34, Num. 1; Jan. 2001.
17. J. Thornburg, D.S. Ensor, C.E. Rodes, P.A. Lawless, L.E. Sparks, and R.B. Mosley. Penetration of Particles into Buildings and Associated Physical Factors, Part I: Model Development and Computer Simulations. Aerosol Science and Technology: Vol. 34, Num. 3; March 2001.
18. Sulman FG. The impact of weather on human health. Rev Environ Health 1984;4(2):83-119.
19. Krueger AP, Reed EJ.Biological impact of small air ions. Science 1976 Sep 24;193(4259):1209-13.
20. Sulman FG. Migraine and headache due to weather and allied causes and its specific treatment. Ups J Med Sci Suppl 1980;31:41-4.
21. Sulman FG, Levy D, Lunkan L, Pfeifer Y, Tal E. New methods in the treatment of weather sensitivity. Fortschr Med 1977 Mar 17;95(11):746-52.
22. Udermann H, Fischer G. Studies on the influence of positive or negative small ions on the catechol amine content in the brain of the mouse following shorttime or prolonged exposure. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg [B] 1982 Apr;176(1):72-8.
23. Goldstein N, Arshavskaya TV. Is atmospheric superoxide vitally necessary? Accelerated death of animals in a quasi-neutral electric atmosphere. Z Naturforsch [C] 1997 May-Jun;52(5-6):396-404.
24. Livanova LM, Levshina IP, Nozdracheva LV, Elbakidze MG, Airapetiants MG. The protective action of negative air ions in acute stress in rats with different typological behavioral characteristics. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 1998 May-Jun;48(3):554-7.
25. Reilly T, Stevenson IC. An investigation of the effects of negative air ions on responses to submaximal exercise at different times of day. J Hum Ergol (Tokyo) 1993 Jun;22(1):1-9.
26. Kosenko EA, Kaminsky YuG, Stavrovskaya IG, Sirota TV, Kondrashova MN. The stimulatory effect of negative air ions and hydrogen peroxide on the activity of superoxide dismutase. FEBS Lett 1997 Jun 30;410(2-3):309-12.
Reviewed by
Brunilda Nazario, MD
May 6, 2002 -- There's something in the air and while it may
not be love, some say it's the next best thing -- negative ions.
Negative ions are odorless, tasteless, and invisible molecules
that we inhale in abundance in certain environments. Think mountains,
waterfalls, and beaches. Once they reach our bloodstream, negative ions are
believed to produce biochemical reactions that increase levels of the mood
chemical serotonin, helping to alleviate depression, relieve stress, and boost
our daytime energy.
Science 101
Ions are molecules that have gained or lost an electrical
charge. . They are created in nature as air molecules break apart due to
sunlight, radiation, and moving air and water. You may have experienced the
power of negative ions when you last set foot on the beach or walked beneath a
waterfall. While part of the euphoria is simply being around these wondrous
settings and away from the normal pressures of home and work, the air
circulating in the mountains and the beach is said to contain tens of thousands
of negative ions -- Much more than the average home or office building, which
contain dozens or hundreds, and many register a flat zero.
"The action of the pounding surf creates negative air ions and
we also see it immediately after spring thunderstorms when people report
lightened moods," says ion researcher Michael Terman, PhD, of Columbia
University in New York.
In fact, Columbia University studies of people with winter and
chronic depression show that negative ion generators relieve depression as much
as antidepressants. "The best part is that there are relatively no side
effects, but we still need to figure out appropriate doses and which people it
works best on," he says.
Vitamins of the Air?
Generally speaking, negative ions increase the flow of oxygen
to the brain; resulting in higher alertness, decreased drowsiness, and more
mental energy," says Pierce J. Howard, PhD, author of The Owners Manual for
the Brain: Everyday Applications from Mind Brain Research and director of
research at the Center for Applied Cognitive Sciences in Charlotte, N.C.
"They also may protect against germs in the air, resulting in
decreased irritation due to inhaling various particles that make you sneeze,
cough, or have a throat irritation."
And for a whopping one in three of us who are sensitive to
their effects, negative ions can make us feel like we are walking on air. You
are one of them if you feel instantly refreshed the moment you open a window
and breathe in fresh, humid air.
"You may be one of them if you feel sleepy when you are around
an air-conditioner, but feel immediately refreshed and invigorated when you
step outside or roll down the car window," Howard tells WebMD. "Air
conditioning depletes the atmosphere of negative ions, but an ion generator
re-releases the ions that air conditioners remove."
In fact, every home has a built in natural ionizer -- the
shower.
But when it comes to springing for that negative-ion generator
you saw advertised in the local paper or on the web, buyer beware, says
Columbia's Terman.
"There is a major problem with advertised units," he tells
WebMD. "Output levels are not ... specified in a way that could advise
antidepressant dose."
And, he says, the cost of apparently equivalent units ranges
from $100 to $1,000.
"The safest course of action, in my opinion, would be to use
units that have been demonstrated effective in our clinical trials and trials
to come," he advises WebMD readers.
Room air circulation, heat and humidity, the proximity of
grounded devices that may emit counteracting positive ions (such as computer
monitors) may affect output levels (of a negative-ion generator), he
explains
"We have tried to minimize the influence of these factors by
adding grounded wrist-straps [commercially available] or grounded bed sheets
[not yet available] for connection to the ionizer," he says.
The possible interaction of negative-air ion therapy and
antidepressant drug or light therapy for seasonal depression has not yet been
investigated, he says. "It stands to reason, for example, that drug ...
dose could be tapered [even to zero], if the patient responds to negative ion
exposure.
"I would advise anyone who experiences clinically significant
depression to try negative-ion therapy only under doctor's guidance, and that
doctors read up on this methodology before OKing such a trial, especially if
the patient is already receiving other treatment," he advises.
What About Allergies and Asthma?
Harold Nelson, MD, professor of medicine at National Jewish
Medical Center in Denver, was so excited when he first heard of negative-ion
generators 20 years ago that he went out and bought one to study among allergy
and asthma patients.
Unfortunately, the findings were "not terribly encouraging. We
couldn't demonstrate anything," he tells WebMD. "I was disappointed. I had high
expectations and they did not pan out, " he says.
The best bet for people with allergies and/or allergic asthma
is to try to eliminate exposures, he says. "If you can't, or if you still have
symptoms, then medication is the next step and fortunately we now have
excellent medications," he says.
Published June 2, 2003.
Negative Ions - Vitamins of the Air?
by Don Strachan and Jim KarnstedtWhen certain kinds of winds begin to blow throughout the world, hospital admissions, suicides, and crime rates skyrocket . One country- Switzerland- even accepts the blowing of the "Foehn" during the commission of a crime as mitigating evidence in court.
These "notorious" desert and sea winds are also linked to minor illnesses and malaise epidemics. Victims’ claims range from sleeplessness, irritability, tension, migraine, nausea, palpitations and hot flashes with sweating or chills, to tremor, vertigo, swelling, breathing difficulty, and frequent intestinal movement. In addition, elderly persons are affected with depression, apathy, and fatigue.
What causes these "witches’ winds," as they’re often called, to differ from others? What do they possess or lack that make them a dread to the lands or oceans they blow across?
Nothing more than an ambulance of invisible, minute particles with an imperceptive electrical charge- positive and negative ions.
According to the experts, positive ions rob us of our good senses and dispositions, while their stimulating everything from plant growth to the human sex drive.
For the uninitiated ions are charged particles in the air, formed when enough energy acts on a molecule- such as carbon dioxide , oxygen, water, or nitrogen- to eject an electron. The displaced electron attaches itself to a nearby molecule, which then becomes a negative ion- neg-ion. The original molecule (minus an electron) is now a positive ion- pos-ion. These ions, in turn, react with dust and pollutants to form larger ions. Small neg-ions -usually no more than 12 gaseous molecules clustered around a charged atom or molecule- are short-lived and highly mobile.
As long as 1789, the Abbe Bertholon, a European monk, speculated that ions exist and affect people. He recorded the responses of medical patients and normal people to changes in the electrical state of the ambient air. More than a century later, in 1899, two scientists named Elster and Geital proved the existence of ions. Only since the 1930s have researchers been probing their secrets.
In nature, ions are formed in a variety of ways. About half are created by radioactive gases. Radioactive substances in the soil, cosmic rays, ultraviolet rays, air flow friction, falling water and plants all produce the other half. For example, they stream off the leaves of plants, most notable pines and asparagus ferns.
Ions are apparently also created by the phenomenon of "subterranean suspiration." As Fred Soyka, author of The Ion Effect, told the first Ions and Light Conference held this summer in Atherton, California. "Solar and lunar influences cause the water table to rise, forcing air out of the earth." This prompted Federal Aviation Administration research psychologist, Bruce Rosenberg, to charge the earth with having "bad breath." Being negatively charged, he said, "it breathes positive ions."
Normally only about one atom in 100,000,000,000,000,000 is ionized, making a total of maybe 1000-2000 ions per cubic centimeter (that’s like a handful of planets floating in a circle 4 billion miles in diameter). These are usually balanced pretty evenly between positive and negative, with a slight edge toward positive. "However, the normal may not be the optimal," Fred Soyka told New Realities. "On the seashore, where water is always falling, you have about 2000 negative to 1000 positive. That seems to be the ratio that human beings respond to most favorably."
We have all experienced this positive effect, regardless of our proximity to waterfall or the ocean. Every home has a built-in, natural ionizer- the shower. Our daily bath rituals are, in effect, the practice of preventive medicine. Research has shown that falling water creates thousands of negative ions by splitting otherwise neutral particles of air, freeing electrons to manifest their vitalizing function. These electrons join up with smaller air particles, thus giving them a predominantly negative charge.
Waterfalls have always been the favorite habitat of mystics and artists. The inspiration and romance generated at places like Niagara Falls and Yosemite have a direct relationship to the lowering of serotonin levels in the blood, caused by the waves of negative ions from the spray of these falls.
Those notorious desert and sea winds mentioned previously raise the ion count, but over-balance the positive- up to a ration of 33 to 1 positive. As the winds blow through arid areas, they stir up dust and the neg-ions are leeched out. In Israel such winds are called the Sharav; in the Alps the Foehn; along the Mediterranean the Sharkiye (called the Sirocco in Italy and the Xlokk in Malta); in Africa the Simoon, France, the Mistral. There’s the Boras of the Adriatic, the Karaburan of the Gobi, the Zondi of Argentina, the Tramontana of Spain. In the U.S., the Chinook plagues the Rockies and the Santa Ana the southern California desert. Still other winds pos-ionize India and Australia. But whatever their name, throughout the world, they are known to blow no good.
One might postulate that the culprit is really humidity, wind or temperature changes, not positive ionization. That has been considered, but doesn’t account for the fact that weather-sensitive people react to the approaching Sharav 12 to 24 hours before meteorological instruments do. Positive ionization remains the culprit. So much for natural pos-ions.
The really lethal doses of pos-ions lie within our polluted cities, which William Radley, president of Bio-Environmental Systems, refers to as "ion prisons." Car exhausts, factory fumes, tire dust, cigarette smoke, cooking and heating fumes, dust and soot gobble up neg-ions, either neutralizing or positively charging them. Inside, steel and concrete building act as electro-magnetic Faraday cages, absorbing the charges of negative ions. Synthetic building materials, clothing and furniture covering eat up more; so do the metal ducts covering heating and air conditioning outlets. The positive static charge of plastics takes care of the rest so that in a typical interior, the neg-ion count may be below 100 per cubic centimeter. (the minimal amount for optimum human functioning is about 1000/ccm.) In the words of Dr. William Rea, Chief of Surgery at Brookhaven Medical Center in Texas, "Houses don’t breathe like they used to."
Several people have investigated the mechanisms of pos-ions debilitating effects. According to the Russian ion pioneer Vasil’yev, ions act on the endings of pulmonary afferent nerve fibers, altering the functional state of the central nervous system and through it, the peripheral organs. Sulman et al (1970) found that weather-sensitive people excrete more of the neuro-hormone serotonin than non-sensitive people. Serotonin is secreted by the pineal gland and the intestines. It affects sleep, mood, nerve impulses, blood-clotting and contraction of smooth muscles. LSD effects are caused by serotonin inhibitor and chronic serotonin depletion is characteristic of some types of mental anomalies.
Sulman’s work supports the findings of American ion dean Dr. Albert P. Krueger, who discovered that the specific negative ion of oxygen -O- speeds up the rate at which serotonin is oxidized in the bloodstream.
Krueger also found that pos-ions slow the sweeping action of the tiny hairs in our throats form 900 to 600 beats per minute and cut mucus flow, thus lowering our resistance to airborne allergens. For example, the pos-ion carbon dioxide (CO2) causes contracture of the back tracheal wall. Pos-ions also cause vasoconstriction and increased respiration rate.
Oddly enough, notes ion author Soyka, "About five percent of the population seems to react well to a positive charge. They feel euphoric."
If pos-ions are the bad guys, neg-ions wear white hats and shoot silver bullets. Their beneficial effect was first discovered in 1932 by Dr. C.W. Hansell at RCA Laboratories. Dr. Hansell was startled by the violent mood shifts of a co-worker who sat beside and electrostatic generator. He observed carefully and discovered that his colleague was ebullient when the machine produced neg-ions, morose when it made pos-ions.
Subsequent researchers (mostly abroad) have found that neg-ions reduce neurosis and anxiety, heighten appetite and thirst and stimulate sexual behavior. They improve performance of voluntary movements: 81.2 percent of drivers with neg-ion generators scored in the top half on reaction time. And in school they sharpen mental functioning and reduce error rates. After a year with neg-ion generators in their classrooms, a group of kindergarten teachers reported that their students concentrated better and showed almost no "weather effect." Hyperactive kids were calmer, absenteeism was down (except on Mondays) and the teachers themselves felt less fatigued.
Neg-ions promote alpha brainwaves and increase brainwave amplitude, which translates to a higher awareness level. Neg-ion induced alpha waves spread from the occipital area to the parietal and temporal and even reach the frontal lobes, spreading evenly across the right and left brain hemispheres. All of this creates an overall calming effect.
On the physical side, they have given relief from hay fever, migraine and burn and post-operative pains. Along with the burn pain relief, they lessen infection, dry the burns faster, heal them more quickly and leave less scarring. After operations, not only did 57 percent of Dr. Igho Hart Kornblueh’s patients treated with large do ses of neg-ions (10,000/ccm) feel less pain (as opposed to 22.5 percent of controls), but restlessness and infection were also reduced and healing quickened.
But why are ions therapeutic? Partly because they kill germs. Back in the 1930s, a Russian team headed by A.L. Tchijevski found that large ion doses of either polarity retarded bacteria colony formation on plates. Ionization also sterilized enclosed air. Later experiments duplicating Tchijevski’s work noted an exponential bacteria decay rate of 23 percent per minute for untreated air, 34 percent per minute for air with pos-ions, and 78 percent per minute for negatively charged air. They concluded that the pos-ion decay rate was due to simple bonding of the ions with the bacteria, whereas the neg-ions actually killed them.
Interestingly, animals larger than microbes find neg-ions beneficial. Rats learn better and are less anxious. Mice live longer. (Mice with flu die more quickly if deprived of neg-ions.) Silkworms eggs hatch earlier, larvae grow faster, spinning begins sooner, cocoons are heavier. Chickens lay more eggs and grow more plump. Sheep grow faster and supply more wool.
And in the vegetable kingdom, plant seedlings grow up to 50 percent more when charged. Fruit stays fresh longer: after 10 days, ionized tomatoes were still fresh while untreated controls rotted.
Researchers offer a variety of reasons for ion effects. Dr. Krueger explains that plants benefit from both positive and negative ions because "ions expedite both the uptake of iron and its utilization in the production of iron-containing enzymes.... (and) stimulate the metabolism of ATP in the chloroplasts and augment both nucleic acid metabolism and oxygen uptake."
In humans, most researchers think that neg-ions act on our capacity to absorb and utilize oxygen, accelerating the blood’s delivery of oxygen to our cells and tissues. Dr. R. Gualaterotti of the University of Milan says they make wider cell nuclei with more volume. The weight of evidence supports Krueger’s theory that ions break down serotonin in the bloodstream.
Lest negative ions sound too much like a cure-all, testers report that neg-ions work only so long as they’re being inhaled. As the charge is most readily absorbed through the olfactory nerves, you need to breathe them in through your nose, not your mouth. Dr. Krueger cautions that "the biological (non -clinical) effects produced by atmospheric ions are not dramatic; on the contrary, they tend to be limited in degree."
But that’s atmospheric ions. Artificially generated ions are another story. Just as positive ions can be generated artificially by pollution, so can negative ions be man made- with negative ion generators. It’s true, you can’t plug in an ionizer at night and expect new muscles in the morning. But their effects are not always subtle. "People are allergic to the Twentieth Century," says Bio-Environmental Systems President William Radley. "Our architects and interior designers are poisoning us. Some people are so sick or so intolerant of chemical that sometimes the results of ionization are quite dramatic.
Since the 1950s, manufacturers have produced dozens of ion generators for laboratory and home use. Early machines ionized atoms and molecules via high-voltage electrical fields, incandescent materials, ultraviolet light, x-rays and alpha- or beta-radiation from the isotopes. The output of the electrostatic, incandescent, and ultraviolet generators tended to deteriorate rapidly. In addition, electrostatic and ultraviolet machines produced ozone, a toxic oxygen allotrope, as a by-product.
Dr. Krueger used tritium-based generators during the ‘50s. Tritium is a betaradiating hydrogen isotope with a half-life of 12.5 years. A minute amount of the gas is sealed in zirconium and deposited on a stainless steel foil. An electrical potential difference varying from 300 to 2000 volts DC is used to separate pos-ions from neg-ions before they recombine in the plasma. Tritium machines allow precise dosages, but unfortunately tritium is so dangerous that it’s illegal (except in fusion power plants). Thus, the tritium generators manufactured during this period were seized by the FDA.
During the 1960s, ion collectors drew air through an electrostatic field between parallel plates or concentric cylinders; the ions were collected on the plates.
Present ion units apply a high-voltage electrical signal directly to the air to create an intense electric field around the emitters.
Why not set up a monster ionizer over Manhattan? Well, a safety dictates a size limit. Dr. Robert Massy of the University of the Trees reported at the Ions and Light Conference that, whereas a 5,000 volt machine produces less than .05 parts per million of ozone (the limit allowed by the FDA), extremely high-voltage units invariably fail to meet standards.
Although most people in the U.S. are not ion-wise, generators have been popular elsewhere in the world for decades. In World War II, Luftwaffe planes were Negatively ionized by electric field generators, in order to reduce pilot fatigue. And it worked! (Electric field generators are like female ion generates: instead of ejecting ions, they attract them.) Germany and USSR use them in government buildings, hospitals, schools, factories, restaurants, health spas, beauty salons, homes, offices, cars and trucks. In Canada, Fred Soyka notes, "Ionization has become a household word. My book became a best-seller and innumerable articles have come out."
The U.S. has equipped nuclear submarines with ion machines. Ionizers are being used industrially in auto spray paint booths, food processing plants, grain storage bins and chemical spray factories.
Architects and designers are beginning to see the health benefits from fountains and rooftops solariums placed in urban environments, echoing the wisdom of their forefathers in the Roman culture. The growing recognition of our biological needs amidst our artificial interiors is opening up whole new industries aimed at replicating nature indoors.
In addition, we could all take Rosenberg’s advice and wear underwear of polyvinyl chloride to attract neg-ions. From BVD’s to PVC’s then, it’s the negative ion generation.
Several machines are now in the market for home and office use ranging in cost from about $70 to several thousand dollars. You just plug them in and they ionize away. But, here are some considerations to keep in mind. If something or someone is between you and the generator, the ion count around you will drop. If you and the machine are in contact with the same dielectric material (as, for instance, if it and your arms are on the same desk), a charge will build up between you and it, and this charge will repel ions. (Supposedly this doesn’t happen with the latest machines.) Also, you own static charge will often repel ions, especially in dry, indoor wintertime air. Synthetic clothing absorbs ions: wear cotton or wool, which have neutral charges.
At the Ions and Light Conference, Fred Soyka told New Realities of some in-progress Swiss research on ion machine frequencies. Frequencies of 60-100 Hz (cycles/sec) are stimulating to a person, while less than 25 Hz are relaxing. "If you have 60-100 frequency machine,:" Soyka says, "you may have trouble sleeping well with it on. Manufacturers ought to look into machines with adjustable frequency ranges. Some European machines already modulate frequency, so people can dial their needs electrically."
A problem with ionizers has been determining their effectiveness. A typical generator may supposedly churn out 100 billion ions per second. But how many of them survive a yard past the machine? Ion counters do exist, but until now no store or salesperson selling generators has had one around. Inexpensive units are now on the assembly line. Ion counters must be used carefully: within a room the ion concentration varies a lot, depending on how far you are from the generator, from conducting wall, from charge buildup on insulating walls, from curtains or draperies.
Poor measurability partly explains why shoddy machines have been marketed (and confiscated by the FDA) in the past. Today, regrettably, the field is still not without its quacks. According to Bruce Sullivan, president of Environmental Sciences Corp. "Some people are selling generators for thousands. One company calls its machine The Air Doctor."
Advanced technology has eliminated most problems associated with previous ion devices, and as such there are more on the market today. Moreover, it is now possible to create higher voltages with lower current, thereby reducing or eliminating the production of ozone (Federal law prohibits more than .05 parts per million ozone level). So to ensure that a device meets the buyer’s needs, one should carefully examine the manufacturer’s literature.
In addition, buyers should look for a warranty on parts and labor, including a description of the room size affected by the machine, and even a money-back trial period offer. A list of authorized service centers should also be provided to the consumer. So caution is still the watch-word since industry standardization has yet to be instituted, although industry standard for ion measurement and output are currently being drawn up by several manufactures.
The first call for some kind of industry standards was issued by ion pioneer Igho Hart Kornblueh back in 1961: "Standardization of the generating and metering equipment by an independent authority would terminate the hasty and regrettable trend to market ion generators of questionable safety, quality and output."
Today Fred Soyka echoes his words: "Measuring the sending capacity of these machines is very important. You should by able to say, like when you buy a 60-watt light bulb. I’m getting an ionizer of this and this capacity. And to correlate that to room sizes."
A giant step was taken at the Ions and Light Conference, where the International Bio-Environmental Society was formed to set up standards and regulations within the industry. "We’ve already gone through our Inquisition on ionization," said president Bruce Sullivan, "We don’t need another one." The Association is building a box within which the ion output of different machines can be counted at a standard distance and humidity.
Ions have been around for eons. Science has had its eye on the ion for 80 years. But public ignorance, generally non-ionized interiors and lack of generator standards is the hallmark of a science and industry still in its infancy. Dr. E.R. Holiday thinks we know as much about air today as we did about food 70 years ago, when biochemists thought protein, fat, and carbohydrates were all we needed. Then a substance was discovered that prevented rickets: the first vitamin. Ions might well be, as Holiday suggests, "the vitamin of the air."
James Karnstedt is a writer, lecturer and researcher whose interests lie in the field of light, color, sound and ions as they affect human consciousness and health.
Don Strachan, a freelance writer, lives in Los Angeles and is a book reviewer for the Los Angeles Times.
Negative Air Ionization
Negative air ionization has the potential to reduce the concentration of airborne microorganisms. The effect appears to result from the ionization of bioaerosols and dust particles that may carry microorganisms, causing them to settle out more rapidly. Settling tends to occur on horizontal surfaces, especially metallic surfaces, and generally in the area near the ionization unit. Ionization may enhance agglomeration, creating larger particles out of smaller particles, thereby increasing the settling rate. Ionization may also cause attraction between ionized particles and grounded surfaces.In situations where dust may carry microorganisms, negative air ionization can be economical to use to reduce infections. It has been used economically to reduce the incidence of Newcastle Disease Virus in poultry houses (Mitchell 1994). Poultry houses can be notoriously dusty.




TYPICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR ION GENERATORS
|
|
Ion Generation Method
|
Pulse Ionization Field
|
Power Supply
|
9 kV - 15 kV
|
Wattage
|
0.75 - 2.7 W
|
Ozone Production
|
< 0.02 PPM
|
- Gabbay, J. (1990). “Effect of ionization on microbial air pollution in the dental clinic.” Environ. Res. 52(1): 99.
- Happ, J. W., J. B. Harstad, et al. (1966). “Effect of air ions on submicron T1 bacteriophage aerosols.” Appl. Microb. 14: 888-891.
- ICCCS (1992). The Future Practice of Contamination Control. Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Contamination Control, Westminster, Mechanical Engineering Publications.
- Mitchell, B. W. a. D. J. K. (1994). “Effect of negative air ionization on airborne transmission of newcastle disease virus.” Avian Diseases 38: 725-732.
- Mitchell, B. W. (1994). “Effect of negative air ionization on airborne transmission of Newcastle Disease Virus.” Avian Dis. 38(4): 725.
- Phillips, G., G. J. Harris, et al. (1963). “The effect of ions on microorganisms.” Int. J. Biometerol. 8: 27-37.
- Estola, T., P. Makela, et al. (1979). "The effect of air ionization on the air-borne transmission of experimental Newcastle disease virus infections in chickens." J. Hyg. 83: 59-67.
- Kreuger, A. P., R. F. Smith, et al. (1957). "The action of air ions on bacteria." J. Gen. Physiol. 41: 359-381.
- Krueger, A. P. and E. J. Reed (1976). "Biological Impact of Small Air Ions." Science 193(Sep): 1209-1213.
- Lehtimaki, M. and G. Graeffe (1976). The effect of the ionization of air on aerosols in closed spaces. Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Contamination Control, Copenhagen.
- Makela, P., J. Ojajarvi, et al. (1979). "Studies on the effects of ionization on bacterial aerosols in a burns and plastic surgery unit." J. Hyg. 83: 199-206.
- Phillips, G., G. J. Harris, et al. (1964). "Effect of air ions on bacterial aerosols." Intl. J. of Biometerol. 8: 27-37.
- Soyka, F. & A. Edmonds (1991). "The Ion Effect" Bantam Books.
Asthma and Ions
Advanced Research on Atmospheric Ions and Respiratory Problems
by Guy Cramer
Sept. 2,1996
Ions are small particles that take on an electrical charge. In nature we tend to find between a few hundred to a few thousand of these ions per cubic centimeter. The small particles that take on this charge are either negatively charged, positively charged or neutral. In a cubic centimeter of air out over a grass field, we find the ratio is almost balanced between negative ions and positive ions. In other words we are breathing quantities of electricity.
Positive ions are known to make asthma victims worse. Positive ion winds such as the Chinook Wind in Calgary, Alta., Canada and the Santa Ana Winds in Southern California are known to coincide with Asthma attacks. There are many areas around the would known for positive ion winds (times when the ion balance has more positive ions per cubic centimeter than negative ions).
A Doctor treating burn victims with negative ion generators found that those patients who also had respiratory problems - chronic bronchitis or asthma - all reported that negative ion therapy helped them breath more easily. With these findings the Doctor started research into the effects of ions on respiratory ills. This research was carried out at the Northeastern Hospital, at the University of Pennsylvania's Graduate Hospital, and the Frankford Hospital in Philadelphia. He found 63% of patients suffering from hay fever or bronchial asthma "have experienced partial or total relief" because of negative ion therapy. One hospital doctor who worked on the project said later, " They come in sneezing, eyes watering, nose itching, worn out from lack of sleep, so miserable they can hardly walk. Fifteen minutes in front of the negative ion machine and they feel so much better they don't even want to leave."
In Britain two Oxford University statisticians conducted a study among 100 victims of asthma, bronchitis, and hay fever chosen at random from a list of people who had purchased negative ion generators in the hope that it would help their problems. In the end their report was based on interviews with only 74 of the 100. They found that 18 of 24 asthmatics; 13 of 17 bronchitis sufferers; 11 of 12 hay fever victims; and 6 of 10 people afflicted with nasal catarrh reported that negative ion generators had noticeably improved their condition. A few claimed the generator had cured them.
Brazilian Hospitals have commonly used ionizing devices for the treatment of breathing problems, including allergies, following a test involving 36 children with asthmatic allergies. All of them had consistent and in some cases crippling problems before taking negative ion therapy; during the treatment only one of them suffered an allergy attack and afterward all were reportedly cured, at least to the point that they no longer suffered problems so long as they took part in occasional negative ion therapy sessions.
In 1966 at a hospital in Jerusalem, doctors performed a series of tests on thirty- eight infants between two and twelve months old. All suffered to about the same degree from respiratory problems. They were divided into two groups of nineteen, one kept as a control group in a ward without any ion charge and the other where a negative ion generator was in use.
The researchers reported that negative ions without any other treatment - that is, no drugs - seemed to cure attacks of asthma and bronchitis more quickly than drugs, antibiotics included. They also observed that there were none of the "adverse side effects" frequently found when treating such children with drugs. They concluded that the children treated with negative ions were less prone to "rebound attacks" (relapses). As to objectivity, the scientific report said that the tests "demonstrated that the atmospheric ions have an effect on infants, especially those suffering from asthmatic bronchitis." Less scientifically, they found that babies didn't cry as often and as loudly when they were breathing negative ions as they did in normal air. And there is nothing subjective about a bawling baby.

Humidity and Asthma
In humid areas - New York in high summer, for instance, or in Toronto - part of the familiar discomfort is caused by the fact that air becomes ion-depleted. Really humid days are murder for anyone suffering from asthma or any respiratory allergy, and the fact that such people find it difficult to breath in hot, humid air may have less to do with the amount of oxygen in the air then with the massive negative ion depletion. Air electricity is quickly conducted to the ground by the moisture in the air, and what negative ions there are attach themselves to particles of moisture and dust and lose their charge. We have seen how positive ions make breathing more difficult and reduce the body's ability to absorb oxygen; and how negative ions help breathing and improve oxygen absorption. (*NOTE; DO NOT USE HUMIDIFIERS OR VAPORIZERS WITH NEGATIVE ION GENERATORS. NEGATIVE IONS WILL ATTACH TO WATER MOLECULES FROM THE HUMIDIFIER OR VAPORIZER AND CREATE POSITIVE IONS. OUR OWN STUDIES HAVE SHOWN THIS EFFECT.)

Pollen, Pollution and Asthma
The ion count is always low in cities where there's precious little open ground to generate them. Pollution makes a bad situation worse, since it tends to deplete the negative ion count even more. The high pollen count in certain parts of North America each fall cuts even further into the negative ion count, since pollen has the same effect as dust. The end result is that the total ion count in cities is always down to what many scientists consider perilously low levels. As if that weren't bad enough, the normal 5 - 4 ratio of positive ions to negative ions is distorted so that people are, in a sense, victims of positive ion poisoning.

Central Air Conditioning and Heating
Hot or cool air forced through the duct work of most central heating and air- conditioning systems sets up friction that results in the loss of almost all the negative ions and also draws most of the positive ions out of the air as well. Then comes the coup-de-grace: This air with some positive and virtually no negative ions is forced out through vents in to rooms, offices and passages - and as it passes through the vents more friction is set up that generates an additional overload of positive ions. What finally comes out of most heating or air- conditioning outlets in the offices we work in and the rooms we live in is likely to be an overload of positive ions which will upset the mental and physical equilibrium of everyone, not only those of us who are ion sensitive.
Just how bad these systems are depends to a great extent on their design and the material from which the duct work is made. The design or layout of the whole system is crucial. At bends and curves and right-angle junctions the friction between ducts and air increases and has the effect of increasing the number of positive ions in the air. What comes out of the heating and cooling vents in any centrally heated or air-conditioned building is air that is not only low in total ions, but also has a heavy positive ion count when measured against the almost negligible quantity of negative ions. It is because of the design of this duct work that some parts of a building may be more "uncomfortable" to work in then others. That depends on whether you're on the receiving end of air that has passed a particular section of duct work, where there is a sharp bend near the outlet - as the air is forced around bends and corners there is greater friction and a consequent increase in positive ions.

Asthma and Synthetics
Asthmatics or people with emphysema and other respiratory ills often suffer additional agonies because of the cloth they wear, and are just as often unaware of the reason why they suffer. Dr. Bernard Watson, professor of medical electronics at Britain's St. Bartholomew's Teaching Hospital in London, says: "Changing the immediate unhealthy ion environment to help asthmatic means changing everything, clothes, sheets, furniture - just everything." One of his patients a girl at that time of fourteen, who had begun to suffer from serve migraine because of clothing - and then cured it herself. When she grew to adolescence and began to wear, with great pride, nylon bras and panties favored by most women, she began to suffer from occasional headaches for the first time in her life. When she graduated to slips and night-dresses and pretty nylon blouses, she became a full-fledged migraine sufferer. Her local general practitioner could offer neither explanation nor help beyond suggesting the onset of menstruation as a cause. But the girl was bright enough to associate the clothes of blooming womanhood with her problem and promptly abandoned the feminine underwear and nightdresses. Now her clothes are of cotton, which is the only fiber that creates no charge at all, and of natural fibers like wool, which carry little charge of either kind. However, once migraine has taken root it is not easy to cure and Dr. Watson is still treating the girl, in part by suggesting to her parents that certain items of furniture in their home should be removed.
The Director of the Danish Air Ionization Institute, Christian Bach (electrical engineer) has studied the clothes and environments of asthmatics and others who suffer from positive ion poisoning, then pinpoints the offending fabrics and articles that are throwing the ion effect out of balance. Bach and his colleagues have worked with many hospitals in treating many victims of asthma and other respiratory ills.
Bach tells of what has become a classic case history involving a woman who had asthma in her own apartment but not in the homes of friends. Even a negative ion generator was of no help, so Bach conducted what must have been one of the oddest investigations in history: Was the culprit the furniture, the television set, the bedding, the lamp shades? Bach found that the lady's taste ran mostly to modern synthetic fabrics. However, that alone was insufficient to explain the problem, so Back began cross-examining the woman about her housekeeping. He found that her furniture was treated with cellulose and silicone-based furniture finishes. Laboratory tests proved that such finishes, when rubbed with polishing rags and dusters, produce a positive charge. Then he visited the friends in whose home her asthma condition disappeared. There he found that the furniture was hand polished with old-fashioned wax and elbow grease, which produced no static charge at all. Bach coated the victim's furniture with an anti-static compound, told her to buy antique furniture without modern wood treatments, and her asthma attacks ceased.
In all, Bach had by 1967 treated almost 1,000 hay fever and asthma cases whose problems were cured or eased by his "passive therapy" approach. in one case, he says, a man became an asthma victim because his wife bought two new lampshades that led to overproduction of positive ions; In another instance several members of the same family became sufferers because their new television set had a teak cabinet that had been treated with cellulose. He also. He also tells of one instance in which he was called in to help save the fortunes of a chicken farmer. The farmer had two monstrous chicken houses each housing 20,000 chickens. In one of them between 150 and 200 chickens died every week. Bach found that both chicken houses were of identical design and construction, except that the one where the chickens died had a roof lined with sheets of plastic while the other had a roof lined of wood. Whenever there was a change in whether the death rate went up. Bach concluded that when the whether changes affected air electricity the plastic stimulated the production of positive ion overdoses. He treated the roof with anti-static substance, and within weeks the chicken mortality rate was normal in both hen coops.
Bach says like all Scandinavians, the Danes keep their homes spotless, forever flourishing dusters, wielding brooms, pushing vacuum cleaners, and otherwise raising clouds of dust to which negative ions are attracted, and so disappear as physiologically active small ions. It is it would seem, healthier to be a sloppy housecleaner then a meticulous one. At the International Ion Research Conference in Philadelphia in 1961. Dr. Hansell ended his speech by saying that to prevent a buildup of potentially harmful ions the person who comes home from work should promptly take his shoes off and walk around the carpets in their stocking feet. And he added, "My suggestion to the house cleaner is that it is very well known fact that it is very difficult to get a charge from a dirty surface. They should not, I suggest be too house proud."

Respiratory Tract and Ions
In the mid-1960s, Experiments showed that the cilia of the trachea, or windpipes, of small animals are stimulated by negative ions and depressed by positive ions. Human cilia, like those of small animals are microscopic hairs that maintain a whip like motion of about 100 beats per minute while cleaning the air we inhale of dust and pollen and other matter that should not reach the lungs. Subjected to tobacco smoke, which absorbs negative ions, the cilia slow down. Tobacco smoke plus positive ions make this slow-down take place from three to ten times more quickly than does smoke alone. An overdose of negative ions, however, neutralizes the effect of smoke on the cilia. Although this experiment took place in a laboratory and involved mice, rats, and rabbits, the implications are clear: Smoking and other forms pollution that absorb negative ions may also damage the ability of the cilia to clean the air that finally ends up in the lungs. Does that mean their is a relationship between positive ions and the incidence of lung cancer, particularly in smokers? As Bach points out, that is one of the many things about ionization we don't yet know, though scientists are investing the relationship.
The effect of ions on respiration is more obvious. The U.S. experimenters Windsor and Becket gave sixteen volunteer overdoses of positive ions for just 20 minutes at a time and all of them developed dry throats, husky voices, headaches, and itchy or obstructed noses. Five of the volunteers were tested for total breathing capacity, and it was found that a positive ion overdose reduced that capacity by 30 percent. Exposed to negative ions for ten minutes , the volunteers maximum breathing capacity was unaffected. What is significant here is that negative ions did not effect the amount of air breathed, but positive ions made breathing more difficult.

Negative ion generators (sold in North America as Air Purifiers / with negative ion generator). You should only have to pay between $50.00 - $250.00 for a negative ion generator depending on room size, (In certain areas medical covers some of these costs.). Bionaire sells these in Europe, Canada and the United States. they can be found at some Department stores and some drug stores. The plus for someone with respiratory difficulties is the added air purifier with carbon filters. The newer models have a hepa filtration system in them. Make sure you change the filters as directed in the instruction manual.
Negative ion generators are not a cure all. They do cause the body to convert excess serotonin (the antagonist for most of the problems) into a harmless chemical called 5HA ( 5-HIAA ).
If you do have respiratory difficulties and use a negative ion generator in your bedroom at night beware that the negative ion generator will keep you alert and awake longer then you might want. You may wish to only use the air filter at night. Most negative ion generators have an on/off switch for the ion control so you can use only the fan/filter system.
The majority of this report on Asthma and Ions was taken directly form the book;
"The Ion Effect" by Soyka, Fred ( Lester and Orpen Limited, 1977) these references can be found on pages 31, 35, 45, 56-57, 63, 75, 76, 77, 79-80, 84, 85, 90, 128, 129-131.
Special Olympic Report:
Secret Russian Sports Weapon Disclosed
 VANCOUVER, BC - September 21, 2000 (INB) -- Olympians may
benefit from technology derived from the Cold War Era. For decades the Russians
have been secretly using a unique performance enhancement device that has proven
to increase endurance levels by as much as 900%, balance coordination by 300%,
and
VANCOUVER, BC - September 21, 2000 (INB) -- Olympians may
benefit from technology derived from the Cold War Era. For decades the Russians
have been secretly using a unique performance enhancement device that has proven
to increase endurance levels by as much as 900%, balance coordination by 300%,
and reaction time by 100%. In studies conducted by the Soviet Union just after
World War II, negative ion generators were used during training of Track and
Field athletes, Gymnasts, Swimmers and Boxers, as part of a new Soviet policy
decision to dominate international sports.
reaction time by 100%. In studies conducted by the Soviet Union just after
World War II, negative ion generators were used during training of Track and
Field athletes, Gymnasts, Swimmers and Boxers, as part of a new Soviet policy
decision to dominate international sports.Canadian ion scientist, Guy Cramer, has been studying the effects of ions on human behavior for 15 years. In this capacity, he has consulted for the NHL. In 1993 he confirmed that the Russians were still using these negative ion generators with the Russian Red Army and Olympic hockey teams as recently as 1989. This information was verified with former Russian hockey players now playing in the NHL. Naturally, Cramer was intrigued but not surprised by what he had discovered. He points out, "The Russians competed in their first international hockey tournament in 1958, only five years after the Czechs showed them how to play, and they won the world championship by beating the Canadians 7-2 in the final game. They literally skated our boys off their feet!" In the 1972 Summit Series between Canada and the Russians, Paul Henderson commented after the first game, "I worked really hard in training... by this time I was really gasping for air. And I look up and this Russian is standing beside me... not breathing at all... I just felt sick. I knew we'd been sucked in."
This may all sound a little far-fetched for the average sports fan, but the scientific community does recognize significant and measurable effects of ions on human behavior. An excess of positive ions produces detrimental effects both physically (headaches, dizziness, fatigue, circulatory disorders etc.) and mentally (irritation, apathy, anxiety, depression etc). Negative ions are beneficial, and can improve alertness, concentration and overall body function. These findings are based on research with air ions from groups and organizations such as Oxford University, RCA Laboratories, U.S. Air Force, Mercedes Benz, and the Swiss Bank... just to name a few of the more than 5000 studies. Negative ion generators/air purifiers are common household appliances found at many department and drug stores. The U.S. Navy uses these generators on the bridges of their ships to keep the command watch alert and energized.
Cramer's encyclopedic knowledge of ion-related information supports a rather suspicious theory. In his words, "The Americans discovered the Russian negative ion study in 1960, when U.S. intelligence translated the relevant documents (see abbreviated study notes attached). There is some anecdotal evidence that the U.S. may have used positive ions against the Russian Olympic hockey team during the 1980 Winter Olympics held in Lake Placid N.Y. They housed the Russians in a converted prison, and some of the key hockey players and the coach complained of symptoms that are associated with positive ion overdose. These positive ions would have taken away the advantage the Russians had built up training with negative ions. If the Americans used positive ions in the ventilation of the Russian accommodations to limit the Russians, then it is quite feasible that they could have used negative ions with their own U.S. team. The 1980 U.S. Olympic hockey team beat the Russians and went on to win the Gold Medal, which is now remembered as one of the biggest moments in sports history. Interesting, isn't it?"
The Olympic Committee knows about negative ion training, and has never objected to it, primarily because there are no known side effects and its considered natural, "If you trained within 1/2 a mile of Niagara Falls you would be training in high levels of negative ions. Negative ion generators simulate this effect," adds Cramer. Negative ion training certainly has not been widely embraced by athletic trainers, as most believed the Russian study to be propaganda until Cramer confirmed the ongoing undisclosed program recently. The Russians have been taking advantage of their "secret weapon" for years, and have many medals and world championships to show for it.
The Russians used the generators in relative secrecy, keeping the athletes in the dark. Many athletes knew about the generators but it was never disclosed to them what the generators were actually for. The research concluded that the athletes would retain the increased abilities for one month away from the system so they never had to bring it with them to competitions, tournaments or the Olympics.
Cramer tried to encourage the NHL to adopt the Russian system, but soon discovered a new perspective on 'enhanced performance.' "The General Managers were concerned that the improvement in athletic ability would translate into higher salary demands by the players, which current revenue streams could not justify. Needless to say, it's a bit disheartening when you have something that works too well," confides Cramer.
Cramer is now applying his scientific expertise to two entrepreneurial ventures, as a cofounder of HyperStealth Biotechnology Corp., http://www.hyperstealth.com, and United Dynamics Corp., http://www.superforce.com.
HyperStealth produces and markets a unique design of Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers, equipped with a proprietary Passive Negative Ion Generator, for which the company has patent pending. Cramer designed the passive generator after discovering distinct benefits in patient recovery when hyberbaric oxygen therapy was combined with negative ions. The passive negative ion generator is a lightweight unit which doesn't require a power source, that can also be clipped onto or sewn into clothing to combat fatigue and increase alertness, and is currently being tested with athletes, emergency workers and law enforcement officers.
United Dynamics operates a website, http://www.superforce.com, dedicated to forecasting the natural changing ion ratios in the atmosphere and correlating this data to various aspects of human behavior. With these forecasts, our Canadian scientist has been able to accurately predict trends in such activities as hockey and baseball games, golf tournaments, horse races and stock markets. In fact, phantom day trading experiments, ongoing for just over 9 months with certain indexes using his system have yielded remarkable results:
- Dow Jones Index: 38.28% increase (vs. actual market loss of -2.82%)
- S&P 500 Index: 52.69% increase (vs. actual market gain of 3.02%)
- NADSAQ Index: 122.70% increase (vs. actual market loss of -3.89%)
As a result of his work, Guy Cramer has recently been invited to appear on two major TV networks, including PBS's World Business Review hosted by Alexander Haig, and CNBC's DotCom hosted by Mark Hamill. Cramer's unconventional method has been featured in the Financial Post, one of Canada's leading national newspapers, in Grant's Investor, an online financial magazine Chaired by James Grant, the Vancouver Province Newspaper, on the MSNBC website, and is the subject of an article in the September issue of Ticker Magazine, a U.S. finance trade publication. The BBC Radio interviewed Cramer on the subject of the U.S. Presidential Election and the most optimum ion ratio day for voters to decide the fate of each candidate.
With the zero tolerance against banned substances so strictly and justifiably enforced by the Olympic Committee, perhaps it's time for more nations to take a closer look at ion training. With the inexpensive Passive Negative Ion Generator from HyperStealth and knowledge about the most favorable training days from http://www.superforce.com, Olympic Gold may be just a few extra breaths away.
Russian Ion-Athletics Study
Fact: In
static endurance the gymnast
control group had a decreased endurance after 25 days while the negative
ion group showed a 46% improvement. The track and field control group’s
static endurance improved 40% after 25 days while the negative
ion track and field group improved by 192%.
Fact: In dynamic
endurance the gymnasts had no control group but the negative
ion gymnast showed an improvement of 87% over 25 days. In track and field
the control group had a 24% improvement after 25 days while the negative ion group had a 240% improvement.
Fact: In reaction
time the gymnast control group managed to shorten their response time by
11 milliseconds, while the gymnast
negative ion group shortened theirs by 22 milliseconds. The track and field
control reaction time shortened by 4.5% at the end of 25 days, while the track
and field negative ion groups shortened by 16%.
Fact: The equilibrium
results were 80-82% improvement after 25 days for the track and field
control group, while the negative ion
group improved by 145-333%.
Fact: One
of the pertinent observations made after these studies was that the negative ion groups
cheerfulness and vitality were increased notably, along with improvements in
sleep and appetite. Studies showed that the negative ion groups also
utilized vitamins B and C more effectively.
Fact: Studies done with male swimmers and
boxers also showed no increase in muscle strength but negative
ions dramatically improved endurance and quickness.
This is a Forecast and not
guaranteed as actual Ion Ratio data. It should be treated as the same way a
weather forecast is treated, advanced warning that is not always right.

| Positive
Ion Overdose Symptoms: Applies to the Majority of Population |
Negative
Ion Overdose Symptoms:
Applies to the Majority of Population |
| Emotionally Unstable: Boredom, Stress,
Anxiety, Depression, Aggression, Greed...
Increased migrane headaches, joint pain, repiratory
problems; Asthma, Hayfever... Physical decrease for over 75% of the population due to adrenal exhaustion, gets worse with consecutive positive ion days. Excess Adrenaline release: Physical increase for less than 25% of the population, (Only the healthiest and yongest with enough adrenal reserve experiance this). Best Days for Stock Markets as people tend to buy. Stores to hold sales as people will buy more - greed factor. Worst Days for Staff Meetings (low attention spans), School tests (lower IQ scores), Driving (Road Rage increases). Air Quality decreases as pollution is positively charged. Foods of Choice: Cravings for fast food, sugar and caffine. Movie and T.V. choices: Action, adventure and Horror movies will be appeal to viewers. |
Emotionally
Stable: Level headed, Content, Diplomatic, Kind, Compassionate...
Reduction of Health complaints, less sensitivity to
pain. Physical increase for over 75% of the population, gets better with consecutive negative ion days. Increased endurance, balance and improved reaction time. Physical decrease for less than 25% of the population. (while it may not be a bad day for these people their performance may decrease due to the lack of a trigger for their adrenaline. Best Days for sports, meetings, tests. Worst Days for Stock Markets as people tend to not take risks. Air Quality increases as positively charged pollution is neutralized (scrubbed) by negative ions. Foods of Choice: Healthier choices tend to prevail. Movie and T.V. choices: Drama, Clean Comedies and Romantic programs or movies will appeal to viewers. |
Premium Service "Peak Dates" Example: Advanced September
2000 Data.
To order our premium advanced service for $39.95 per month Go HERE
To order our premium advanced service for $39.95 per month Go HERE
For reasons of Homeland
Security we will not provide detailed information regarding the severity of
ion ratios
|
Unauthorized Reproduction,
Exhibition or Distribution of this copyrighted information can result in
Severe Criminal and Civil Penalties under the Laws of your country. Penalties
may result in fines in excess of $100,000 USD per violation. A
cash reward of up to $2,000.00 will be paid for any information which
leads to an arrest and charge due to copyright
infringement.
If you have any information, please Email United Dynamics Corp. at: info@superforce.com
This information is Copyright ©
2000-2010 United Dynamics Corp. ( a Colorado corporation) All Rights Reserved.
United Dynamics Corp. Reserves the Right to discontinue
this service at any time.
This is a Forecast and not guaranteed as actual Ion Ratio data. It should be treated as the same way a weather forecast is treated, advanced warning that is not always right.
This is a Forecast and not guaranteed as actual Ion Ratio data. It should be treated as the same way a weather forecast is treated, advanced warning that is not always right.
January 1, 2010
Is HAARP
responsible for recent worldwide Jellyfish Blooms?
October 15, 2008 SuperForce correctly predicted 7 days prior to the Canadian election that the spread between top parties would widen providing the Conservatives with the win. The SuperForce forecast was made Oct. 9th when opposing parties only trailed in the polls by 4%, Conservatives won with a 12% lead over the closest opposition party. See link below with original forecast.
October 9, 2008 2008 Canadian Election Polls swayed by the Full Moon effect
July 31, 2008 Special Olympic Report: Secret Russian Sports Weapon Disclosed
June 1, 2008 Eco-Week; A simple solution to high Oil Prices
October 15, 2008 SuperForce correctly predicted 7 days prior to the Canadian election that the spread between top parties would widen providing the Conservatives with the win. The SuperForce forecast was made Oct. 9th when opposing parties only trailed in the polls by 4%, Conservatives won with a 12% lead over the closest opposition party. See link below with original forecast.
October 9, 2008 2008 Canadian Election Polls swayed by the Full Moon effect
July 31, 2008 Special Olympic Report: Secret Russian Sports Weapon Disclosed
June 1, 2008 Eco-Week; A simple solution to high Oil Prices
December 19, 2005:
Sharp Corporation
Press Release: Ion Technology Proven Effective Against Airborne Highly
Pathogenic H5N1 Avian Influenza
September 12,
2005:
Sun's String of Fury Continues as 7th Major Flare Erupts
September 7,
2005:
September 7th, 2005 Super
Solar Flare
July 4, 2005:
Wild Blue Yonder: San Francisco Photos indicate Shuttle Columbia was struck by Hyper-Lightning on
Reentry
June 12,
2005:
Jordan Armed Forces
modernization continues with wide scale issue of new KA2 Digital Camouflage
May 26, 2005
Planetary Solar Mirrors
January 23, 2005
HAARP likely not Primary Ionospheric
array in Alaska Companion
site to topical information of interview with Art Bell on Coast to Coast
Radio this evening
December 19, 2004
Police Units in the Kingdom of Jordan to be issued new Advanced
Digital Urban Camouflage
December 8, 2004
Large areas
of Mars now protected from future commercialization
October 8, 2004:
National
Counter-Terrorism Center selects TACAM Camouflage as their Exclusive
Official Pattern
October 5, 2004
"MilTex" Millennium Texture Series Camouflage™
July 13, 2004
Dual Texture -
U.S. Army
digital camouflage
April 16, 2004: Positive
Ion Ban Proposal
Feb 20, 2004:
Breaking News:
Developer of SuperForce.com Algorithm is issued Patent for HyperStealth
"Passive Negative Ion Generator"
Feb 21, 2003
Three Years of back-testing the
SuperForce.com algorithm on 600 stocks
Feb 9, 2003
Shuttle Columbia Disaster: Wrong Place,
Wrong Time! (updated April 28, 29, May 1, May 3, May
10, 2003 & Jan, 19, 2005)
January 11, 2003 Behavioral Economics!November 6, 2002 Predicting Indexes: 34 months of back testing the SuperForce Algorithm with the AMEX, DOW, NASDAQ, Russell 2000, NYSE, S&P and Philadelphia Major Indexes October 30, 2002 Predicting Volatility
May 13, 2002 SuperForce Top 100 lists for 596 companies
Feb 28, 2002 SuperForce Top 100 lists for 600 companies
Feb 7, 2002 Special Olympic Report: Secret Russian Sports Weapon Disclosed
Jan 29, 2002 Markets fall due to rare Solar Shock Wave
Earnings Warnings and Stock Performance vs. Ion Ratios
SuperForce.com Canadian Top 20 Lists: TSE 35 Top 35 companies on the Toronto Stock Exchange
SuperForce Currency Trading 2001 Tracking 16 world currencies
SuperForce Premium Trading method with the Dow 30 Stocks for 2001
SuperForce Top 20 list for Dec 2001 and Volatility Index Correlation
SuperForce.com Special Report: HAARP Defensive Economic Warfare SuperForce.com Report: Ions Threaten Stock Market Fundamentals
January 11, 2003 Behavioral Economics!November 6, 2002 Predicting Indexes: 34 months of back testing the SuperForce Algorithm with the AMEX, DOW, NASDAQ, Russell 2000, NYSE, S&P and Philadelphia Major Indexes October 30, 2002 Predicting Volatility
May 13, 2002 SuperForce Top 100 lists for 596 companies
Feb 28, 2002 SuperForce Top 100 lists for 600 companies
Feb 7, 2002 Special Olympic Report: Secret Russian Sports Weapon Disclosed
Jan 29, 2002 Markets fall due to rare Solar Shock Wave
Earnings Warnings and Stock Performance vs. Ion Ratios
SuperForce.com Canadian Top 20 Lists: TSE 35 Top 35 companies on the Toronto Stock Exchange
SuperForce Currency Trading 2001 Tracking 16 world currencies
SuperForce Premium Trading method with the Dow 30 Stocks for 2001
SuperForce Top 20 list for Dec 2001 and Volatility Index Correlation
SuperForce.com Special Report: HAARP Defensive Economic Warfare SuperForce.com Report: Ions Threaten Stock Market Fundamentals
Year 2000 Review |
If the any of the dials move into the yellow, orange or red then there is a chance that positive ion ratios could be increasing and the stock market indexes are going up. If the dials remain in the green then the forecast applies. This page will auto-refresh every fifteen minutes to keep the dials up-to-date. If no arrows appear on each dial then the satellite is temporarily not receiving or transmitting data.
|
Geomagnetic
storms are a natural hazard, like hurricanes and tsunamis. Severe geomagnetic
storms cause communications problems, abruptly increase drag on spacecraft, and
can cause electric utility blackouts over a wide area. The location of ACE
spacecraft gives about a one hour advance warning of impending geomagnetic
activity.
|
Other United Dynamics Corp. Internet sites:
 United
Dynamics Corp. presents
PoliceOps.com This service for worldwide Law Enforcement agencies to
utilize, plan and prepare in advance for;
Expected high
volume, high volatility shifts for general duty officers. Allowing for
better control on these specific days of high-risk tactical situations,
crisis
resolution,
negotiations... for Emergency Response Teams and Special Ops. United
Dynamics Corp. presents
PoliceOps.com This service for worldwide Law Enforcement agencies to
utilize, plan and prepare in advance for;
Expected high
volume, high volatility shifts for general duty officers. Allowing for
better control on these specific days of high-risk tactical situations,
crisis
resolution,
negotiations... for Emergency Response Teams and Special Ops.
|
Long thought to be random, human behavior and athletic
performance, have turned out to be predictable. Through at least five
overlapping advanced geophysics and astrophysics cycles, these changes can
be forecasted ahead of time. These changes would have been discovered long
ago if 100% of the population was affected the same way, however,
approximately 75% of the population are affected one way and about 25% are
somewhat or oppositely affected due to brain hormones compensating for the
problem.
 |
| La ionizzazione pulisce l'aria ! |

Questo commento è stato eliminato dall'autore.
RispondiEliminaQuesto commento è stato eliminato dall'autore.
RispondiEliminaWow what a great blog, i really enjoyed reading this, good luck in your work. Veri Shades
RispondiElimina